Invest 30 seconds...
...for what may lead to a life altering association!
Help Line
- +91.8800.2828.00 (IND)
- 1030-1830 Hrs IST, Mon-Sat
- support@expertsglobal.com
...for what may lead to a life altering association!


Graphics Interpretation questions in the GMAT Data Insights section require you to analyze information presented in visual formats such as bar graphs, line charts, pie charts, scatterplots, and statistical diagrams. Each set contains two questions that test your ability to interpret patterns, extract insights, and make logical conclusions from the graphic.
To experience all question types on the GMAT, take a free full-length GMAT mock test
Graphics Interpretation questions in the GMAT Data Insights section reflect real-world business tasks. In many professional settings, decisions must be made by interpreting visual data, such as financial charts, sales reports, or market segmentation diagrams. The GMAT uses this format to assess your ability to process such data accurately, quickly, and logically. This article explains what Graphics Interpretation questions are, the skills they test, strategies to solve them, and the common mistakes to avoid. Whether you are beginning your GMAT preparation or aiming to fine-tune your performance, this guide will help you approach Graphics Interpretation questions with confidence and clarity.
Graphics Interpretation (GI) questions are built around a single visual. This could be a bar chart, pie chart, scatterplot, line graph, or another statistical graphic. Beneath the graphic, you will find two separate questions. Each question presents a sentence with one or two blanks. For each blank, you must choose the best option from a drop-down list of three choices.
These questions test your ability to:
This format is designed to simulate how managers, analysts, and consultants work with data in real life. A correct answer will rely entirely on the information shown in the graphic and not on any outside knowledge.
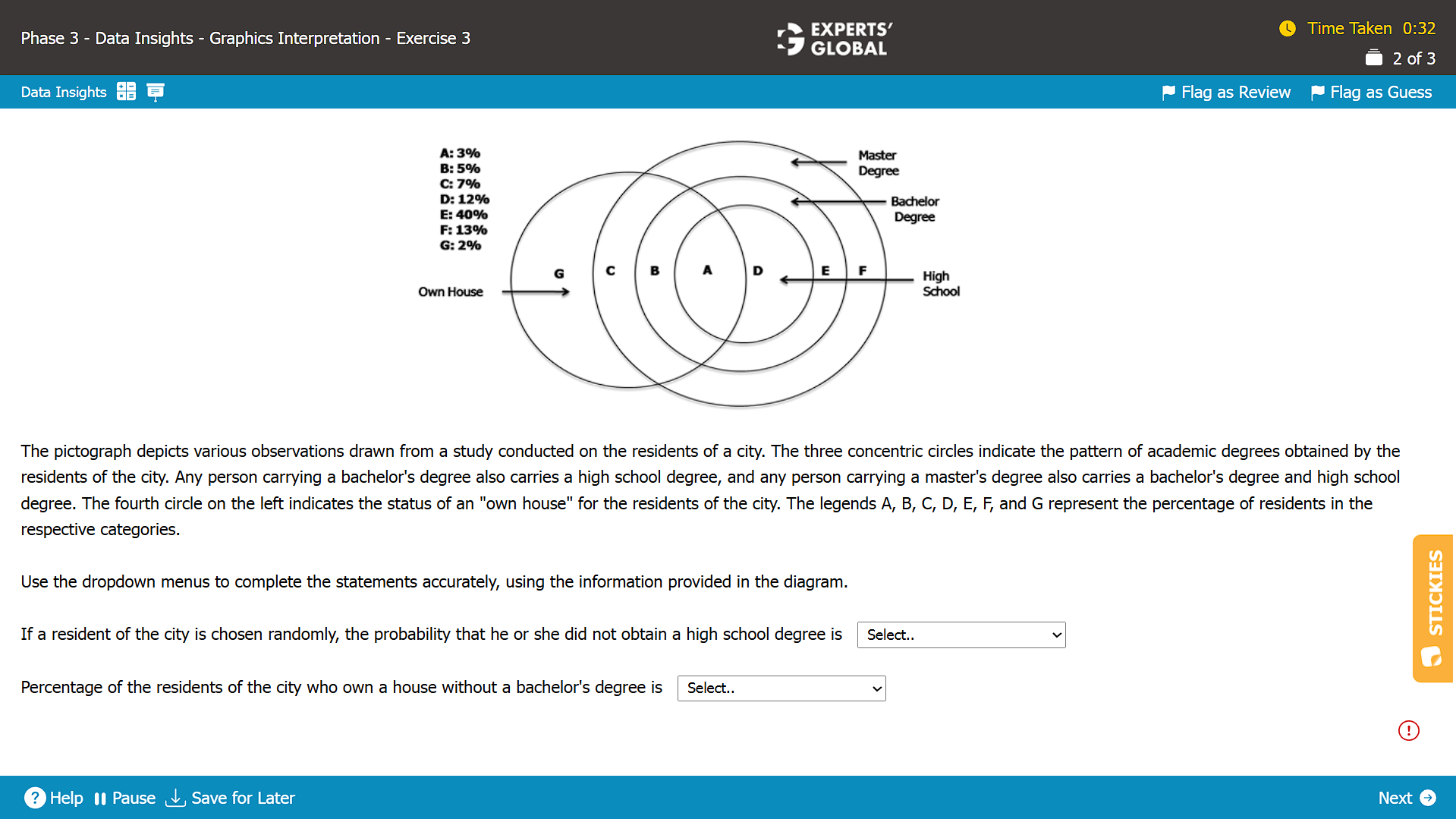
Correct Answer: 20% and 5%
Graphics Interpretation questions evaluate a set of analytical and reasoning skills, including:
You must accurately read values and relationships from bar heights, line intersections, segment sizes, and other visual cues.
You may be required to calculate ratios, percentages, or averages using the numbers from the graph.
These questions often ask you to compare categories, time periods, or variables in a logical and structured manner.
You must observe scales, axes, and labels closely. A small difference in a graph’s layout can completely change the meaning of the data.
Many graphics are used to test your ability to observe patterns and trends and then draw valid conclusions from them.
Each answer must be supported directly by the visual data. The correct choice is often not the most obvious one, but the one most precisely supported by the graphic.

Seek quick GMAT prep? Explore our GMAT crash course
The visuals used in GI questions can take several different forms. The most commonly used formats include:
Each format has its own logic and structure. Familiarity with each of these types helps in recognizing patterns and performing calculations with greater ease.
A strategic approach is essential for efficiency and accuracy. The following approach will help you maximize your performance:
Before looking at the questions, examine the chart’s title, axis labels, units of measurement, and legend. This context helps you avoid misinterpretations later.
Determine what the graph shows. Does the x-axis represent time? Does the y-axis show quantities, percentages, or ratings? Is the scale linear?
Each question includes a sentence with one or two blanks. Take each blank separately. Look back at the graph and identify the relevant data point or relationship before choosing an answer.
Only estimate when the answer options are clearly different. If the choices are close in value, you must read the exact numbers from the graphic.
If unsure, eliminate any choice that is clearly incorrect based on the graphic. Narrowing down choices increases your odds even when you are uncertain.
Confirm your selections by cross-checking with the graphic. Make sure the choice aligns with the actual data rather than your initial impression.
To perform well on Graphics Interpretation questions, avoid the following pitfalls:
Always check whether the axis is showing data in thousands, percentages, or absolute numbers. Misreading units leads to incorrect answers.
Candidates often jump to the questions without fully understanding the chart. Take a moment to absorb the visual before proceeding.
Many graphics use colors, symbols, or labels to distinguish categories. Ignoring these leads to confusion.
Only base your answers on what is visible in the graphic. Do not assume causes, trends, or intentions unless the data directly supports them.
Subtle differences in color shades, axis ranges, or data labels can carry significant meaning. Read everything carefully.
At Experts’ Global, we recommend a three-stage preparation model: Understand, Practice, and Master. This model is designed to help you build capability gradually and effectively.
Begin by studying the types of graphics used in the GMAT. Learn how to interpret bar graphs, line charts, pie charts, and scatterplots. Pay attention to how the GMAT uses these visuals to test mathematical and logical reasoning. Identify traps such as misleading axes, overlapping data series, or inconsistent categories. Focus on developing deep familiarity with the format, rather than speed.
Once the foundational understanding is in place, practice extensively. Use official GMAT resources and high-quality third-party questions. Work on interpreting the visuals accurately and quickly. After each session, review both correct and incorrect responses. Identify whether any error resulted from misreading the chart, using the wrong formula, or overlooking a key detail. Over time, your agility and precision will improve.
In the final stage, incorporate Graphics Interpretation learnings into your timed GMAT mock tests. This helps you develop endurance and calm focus under real test conditions. Pay attention to how you manage your time and whether you remain methodical. Analyze your mistakes after each test and work to eliminate recurring errors. With enough practice, you will approach these questions with steady confidence.
A proficient MBA admission consulting team can guide you from the early stages of GMAT preparation through to building your profile and crafting strong applications. If you start early, the team can help you approach GMAT preparation including the GI questions with clarity, avoid common missteps, and stay motivated throughout. Most importantly, the team can help you enrich your profile alongside GMAT prep and help align your profile with your career goals, making your overall journey smarter and more successful.
Graphics Interpretation questions on the GMAT test your ability to convert visual data into insight. These are the same skills required in business roles where professionals must draw conclusions from sales charts, financial reports, and market analysis. With the right approach and consistent effort, you can develop the clarity, discipline, and control needed to succeed in this format. Treat each question as an opportunity to sharpen your thinking and demonstrate your analytical capability. For structured and comprehensive support across all GMAT question types, explore the GMAT Online Prep Course by Experts’ Global.
Build your best case through our GMAT prep course online and B-school admissions bundle