Invest 30 seconds...
...for what may lead to a life altering association!
Help Line
- +91.8800.2828.00 (IND)
- 1030-1830 Hrs IST, Mon-Sat
- support@expertsglobal.com
...for what may lead to a life altering association!


The verbal section on the GMAT is one of the three sections on the exam and therefore contributes to one third of your overall score. Along with this direct contribution, the skills developed during verbal section preparation also support performance in roughly 50% of the Data Insights section. For this reason, structured and end to end coverage of all GMAT verbal concepts is an essential part of any dependable GMAT prep course. The GMAT verbal section includes two question types: reading comprehension (RC) and critical reasoning (CR). Each question presents a passage or an argument followed by multiple answer choices, out of which only one option is correct. Your task is to read carefully, evaluate the information and reasoning presented, and identify the answer choice that best meets the requirement of the question.
On this page, we provide a brief introduction to the broad topics that appear in the GMAT Verbal section and present reading comprehension and critical reasoning sample questions organized by question type. These sample questions offer a firsthand experience of how GMAT verbal questions appear across different passages, arguments, and reasoning situations, and how they test the required skills. Ensure due learning from this rich resource and apply these learnings in subsequent GMAT drills, GMAT sectional tests, and GMAT full-length mock tests. Happy practicing!
On the GMAT, Reading Comprehension gives you a dense passage with a few smart twists, and then three or four multiple choice questions with exactly one correct answer. You usually see about four passages, which puts roughly 13 to 15 of the 23 Verbal questions in the RC bucket. That fact alone makes RC a non-negotiable part of your Verbal plan and your overall GMAT plan. Here is the real win: strong Reading Comprehension trains you to absorb, filter, and analyze information fast. That skill shows up everywhere, across sections and question types. So when you get better at RC, you do not just raise your RC score, you raise your entire GMAT game.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key Reading Comprehension concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT Reading Comprehension Prep
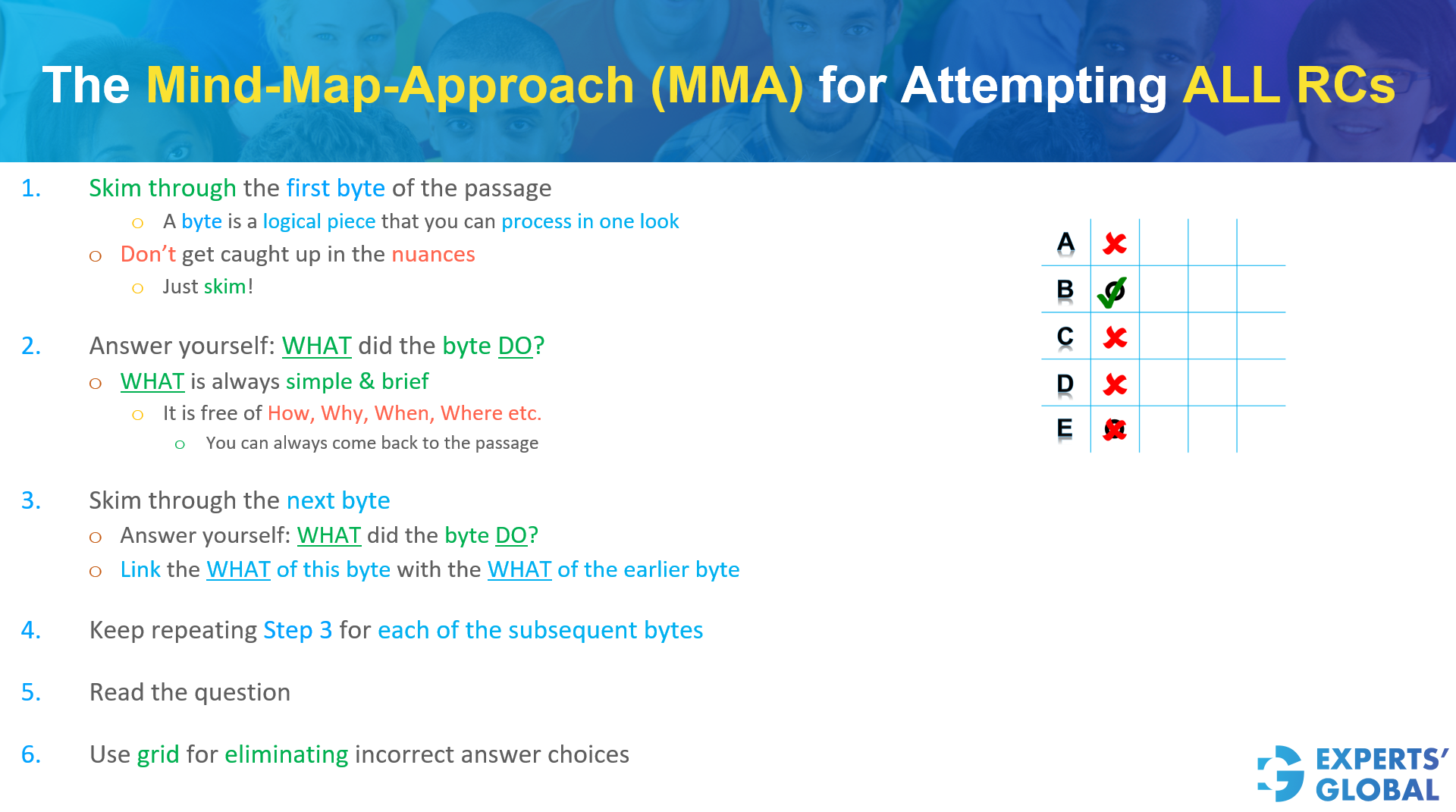

Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
The first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks” and the second paragraph mentions that the Basel III accord seeks to lower risk exposure by “developing a consistent and transparent capital base” and aims at ensuring that any losses are “cushioned by high quality capital”. The passage states that both the Basel II and Basel III recommendations were developed to address the issue of banks’ risk and both recommendations addressed the issue by mandating the banks to create a reserve “capital”. Each answer choice needs to be carefully evaluated in light of the information presented in this context.
A. The passage makes no mention of the amount and number of loans given by banks as a factor in the recommendations of any Basel committee. Furthermore, the first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement” and the second paragraph mentions that the Basel III accord seeks to lower risk exposure by “developing a consistent and transparent capital base”; both the Basel II and Basel III recommendations addressed the issue of banks’ risks by mandating the banks to create a reserve “capital”; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
B. Trap. Although the first paragraph mentions that “The Basel committee was established in the 1970s with the aim of streamlining operations of the banks globally”, the paragraph neither mentions nor suggests “interaction among banks globally”. Furthermore, the first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement” and the second paragraph mentions that the Basel III accord seeks to lower risk exposure by “developing a consistent and transparent capital base”; both the Basel II and Basel III recommendations addressed the issue of banks’ risks by mandating the banks to create a reserve “capital”; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
C. Trap. The paragraph makes no mention of “standardization of banking operations in developing countries”. Additionally, the first paragraph mentions that “Before 2008, the Basel committee had no representatives from the developing world” and the second paragraph mentions that “Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions”; these references to the “developing countries” relate to the failure of Basel II and a potential challenge of Basel III recommendations respectively, but none relates to the aim of any Basel recommendation. Furthermore, the first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement” and the second paragraph mentions that the Basel III accord seeks to lower risk exposure by “developing a consistent and transparent capital base”; both the Basel II and Basel III recommendations addressed the issue of banks’ risks by mandating the banks to create a reserve “capital”; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
D. Correct. The first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks” and the second paragraph mentions that the Basel III accord primarily seeks to lower risk exposure by “developing a consistent and transparent capital base” and aims at ensuring that any losses are “cushioned by high quality capital”; the passage states that both the Basel II and Basel III recommendations were developed to address the issue of banks’ risk and both recommendations addressed the issue by mandating the banks to create a reserve “capital”; in other words, both Basel II and Basel III were developed to reduce financial risk of banks by ensuring access to capital, as the answer choice mentions.
E. The first paragraph mentions that “Basel I regulations concentrated on categorizing borrowers with respect to their level of risks”; a framework to evaluate borrowers’ risk levels relates to Basel I recommendations, not to Basel II and Basel III recommendations. Furthermore, the first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement” and the second paragraph mentions that the Basel III accord seeks to lower risk exposure by “developing a consistent and transparent capital base”; both the Basel II and Basel III recommendations addressed the issue of banks’ risks by mandating the banks to create a reserve “capital”; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
D is the best answer choice.

Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
The first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks” and that “The Basel II committee anticipated a safe banking environment due to the presence of a minimum reserve maintained by banks”. It can be inferred that the Basel II committee believed that a minimum reserve maintained by banks would make a banking environment safe, or risk-free. Each answer choice needs to be carefully evaluated in light of the information presented in this context.
A. Although the first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks”, the passage makes no mention that “the same minimum capital requirement would apply to all banks”; so, it cannot be inferred from the passage that the Basel II committee most likely believed that the same minimum capital requirement would apply to all banks. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the Basel II committee believed that a minimum reserve maintained by banks would make a banking environment safe, or risk-free in this context. Incorrect.
B. The passage makes no mention of how the Basel I recommendations addressed banks’ issues; so, it cannot be inferred from the passage that the Basel II committee most likely believed that Basel I recommendations inadequately addressed risk to banks. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the Basel II committee believed that a minimum reserve maintained by banks would make a banking environment safe, or risk-free in this context. Incorrect.
C. Trap. The second paragraph mentions that “The Basel III accord primarily seeks to lower risk exposure by developing a consistent and transparent capital base and thus increasing banks’ liquidity”; “a transparent capital base” is mentioned in the context of Basel III recommendations, not Basel II recommendations; it cannot be inferred that the Basel II committee most likely believed that a transparent capital base is important for a bank’s risk management. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the Basel II committee believed that a minimum reserve maintained by banks would make a banking environment safe, or risk-free in this context. Incorrect.
D. Trap. The first paragraph mentions that “Basel II failed to protect banks and financial institutions from risky lending and investment behaviors”; the “investment behaviors” relate to the investments made by the bank, not the banks’ borrowers; it is incorrect to infer that the Basel II committee most likely believed that investment behaviors of borrowers affect a bank’s risk. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the Basel II committee believed that a minimum reserve maintained by banks would make a banking environment safe, or risk-free in this context. Incorrect.
E. Correct. The first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks” and that “The Basel II committee anticipated a safe banking environment due to the presence of a minimum reserve maintained by banks”; it can be inferred that the Basel II committee believed that a minimum reserve maintained by banks would make a banking environment safe, or risk-free in this context; in other words, the Basel II committee believed that a minimum capital reserve resulted in risk-free banks, as the answer choice mentions.
E is the best answer choice.

Show Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
The first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks” and “The Basel II committee anticipated a safe banking environment due to the presence of a minimum reserve maintained by banks”, but the recommendations’ failure led “to the global economic crisis of 2008” because “Basel II failed to protect banks and financial institutions from risky lending and investment behaviors” and there was no “uniform adoption and implementation of the recommendations of Basel II by most countries”. Each answer choice needs to be carefully evaluated in light of the information presented in this context.
A. The passage makes no reference to “international lending and investments” or their “challenges” in the context of Basel II recommendations or the global economic crisis of 2008. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that Basel II failed to protect from “risky lending and investment behaviors” and there was no “uniform adoption and implementation” of Basel II by most countries. Incorrect.
B. Correct. The first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks” and “The Basel II committee anticipated a safe banking environment due to the presence of a minimum reserve maintained by banks”, but the recommendations’ failure led “to the global economic crisis of 2008” because “Basel II failed to protect banks and financial institutions from risky lending and investment behaviors”; in other words, the Basel II recommendations likely contributed to the global economic crisis of 2008 because they focused on having reserve capital in the event of the risk but did not sufficiently control risky transactions, as the answer choice mentions.
C. Trap. The second paragraph mentions that “Basel III has been developed to address the shortcomings of the Basel II committee recommendations” and “The Basel III accord primarily seeks to lower risk exposure by developing a consistent and transparent capital base and thus increasing banks’ liquidity”; although it can be inferred that the Basel II recommendations did not advocate a consistent and transparent capital base for the banks, the passage does not state this as the deficiency that led to the economic crisis of 2008. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that Basel II failed to protect from “risky lending and investment behaviors” and there was no “uniform adoption and implementation” of Basel II by most countries. Incorrect.
D. The second paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks”, suggesting that a minimum capital reserved is a measure taken for more security of banks and not likely to lead to a global economic crisis. Moreover, the passage makes no mention of “the day-to-day lending” in connection with the economic crisis of 2008. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that Basel II failed to protect from “risky lending and investment behaviors” and there was no “uniform adoption and implementation” of Basel II by most countries. Incorrect.
E. The passage doesn’t connect the shortcomings of the Basel I committee to Basel II recommendations; it cannot be inferred that the Basel II recommendations did not effectively address the shortcomings of the Basel I committee, and so contributed to the economic crisis of 2008. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that Basel II failed to protect from “risky lending and investment behaviors” and there was no “uniform adoption and implementation” of Basel II by most countries. Incorrect.
B is the best answer choice.

Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
The second paragraph mentions that “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. The passage suggests that the central banks in many countries are concerned that increasing the risk reserve as per the Basel III recommendations may have a negative impact on their regular operation. Each answer choice needs to be carefully evaluated in light of the information presented in this context.
A. Correct. The second paragraph mentions that “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”; the passage suggests that the central banks in many countries are concerned that increasing the risk reserve as per the Basel III recommendations may have a negative impact on their regular operation; in other words central banks in most countries are concerned that the Basel III accord may have an adverse impact on banks’ everyday working, as the answer choice mentions.
B. Trap. The second paragraph mentions that “the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord. Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”; although the passage mentions the difficulty in getting Basel III recommendations implemented in most countries, such difficulty is not the concern of the central banks in most countries. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that it indicates that “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. Incorrect.
C. The passage makes no mention of the incompatibility between Basel III risk management proposals and the policies of central banks in most countries; so, it cannot be inferred that the central banks in most countries are concerned about such incompatibility. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that it indicates that “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. Incorrect.
D. Trap. The second paragraph mentions that the Basel III regulation “may not sufficiently address issues associated with the capital ratios of financial institutions”; although the passage mentions the lack of addressing the issues associated with capital ratios of banks, such lack is not the concern of the central banks in most countries. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that it indicates that “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. Incorrect.
E. The passage makes no mention of the inability to define the level of risks as per Basel III recommendations; so, it cannot be inferred that the central banks in most countries are concerned about such inability. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that it indicates that “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. Incorrect.
A is the best answer choice.

Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
The second paragraph mentions three challenges – firstly, “this regulation may not sufficiently address issues associated with the capital ratios of financial institutions”, secondly, “the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord. Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”, and thirdly, “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. The answer choice that does justice to this summary about the challenges of the Basel III accord is the correct answer choice.
A. The second paragraph deals only with Basel III recommendations; so, the main idea of the second paragraph cannot be related to Basel committee recommendations in general. Furthermore, as the mind-map indicates, the second paragraph suggests that Basel III recommendations have challenges; so, the main idea of the second paragraph is related to the overall challenges of the Basel III accord; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
B. Trap. The second paragraph mentions that “Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”; although the passage mentions that most developing countries fail to implement Basel committee recommendations, the discussion on this idea is limited in scope and cannot represent the whole paragraph. Furthermore, as the mind-map indicates, the second paragraph suggests that Basel III recommendations have challenges; so, the main idea of the second paragraph is related to the overall challenges of the Basel III accord; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
C. “Risky lending and investment behaviors” by banks and “economic crisis” are mentioned in the first paragraph, not in the second paragraph. Furthermore, as the mind-map indicates, the second paragraph suggests that Basel III recommendations have challenges; so, the main idea of the second paragraph is related to the overall challenges of the Basel III accord; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
D. Correct. The second paragraph mentions that the Basel III accord’s approach “to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management” is “promising”, suggesting that the author feels positive about Basel III’s approach. Additionally, the paragraph mentions three challenges – firstly, “this regulation may not sufficiently address issues associated with the capital ratios of financial institutions”, secondly, “the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord. Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”, and thirdly, “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. Overall, the author believes that Basel III recommendations have fundamental merit but implementation challenges, as the answer choice mentions.
E. Trap. The second paragraph mentions that “the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord. Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”; although the passage mentions that risk management proposals of Basel III accord are difficult to implement, the discussion on this idea is limited in scope and cannot represent the whole paragraph. Furthermore, as the mind-map indicates, the second paragraph suggests that Basel III recommendations have challenges; so, the main idea of the second paragraph is related to the overall challenges of the Basel III accord; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
D is the best answer choice.

Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
The second paragraph mentions three challenges – firstly, “this regulation may not sufficiently address issues associated with the capital ratios of financial institutions”, secondly, “This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord. Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”, and thirdly, “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. The author concludes the paragraph by stating that “Despite the improvements made on the Basel III accord, its future remains uncertain”. It can be inferred that the author sees Basel III accord as “promising” and with “improvements”, but the author is “uncertain” about its success. Overall, the author’s attitude is leaning towards uncertainty or doubt. The answer choice that does justice to this thought is the correct answer choice.
A. The second paragraph states that “This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord” and that “Despite the improvements made on the Basel III accord, its future remains uncertain”; it can be inferred that the author sees Basel III accord as “promising” and with “improvements”; so, the author’s attitude towards Basel III accord is not “dismissive”. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the author’s attitude is leaning towards uncertainty or doubt. Incorrect.
B. Correct. The second paragraph mentions three challenges – firstly, “this regulation may not sufficiently address issues associated with the capital ratios of financial institutions”, secondly, “This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord. Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”, and thirdly, “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”; the author concludes the paragraph by stating that “Despite the improvements made on the Basel III accord, its future remains uncertain”; it can be inferred that the author sees Basel III accord as “promising” and with “improvements”, but the author is “uncertain” about its success; so, overall, the author’s attitude is leaning towards uncertainty or doubt; in other words, the author’s attitude is skeptical, as the answer choice mentions.
C. The second paragraph states that “This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord” and that “Despite the improvements made on the Basel III accord, its future remains uncertain”; it can be inferred that the author sees Basel III accord as “promising” and with “improvements”, but the author is “uncertain” about its success; so, the author’s attitude towards Basel III accord is not “applauding”. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the author’s attitude is leaning towards uncertainty or doubt. Incorrect.
D. The second paragraph states that “This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord” and that “Despite the improvements made on the Basel III accord, its future remains uncertain”; it can be inferred that the author sees Basel III accord as “promising” and with “improvements”; so, the author’s attitude towards Basel III accord is not “depreciative”. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the author’s attitude is leaning towards uncertainty or doubt. Incorrect.
E. The second paragraph mentions that “Despite the improvements made on the Basel III accord, its future remains uncertain”; it can be inferred that the author is “uncertain” about Basel III accord’s success; so, the author’s attitude towards Basel III accord is not “confident”. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the author’s attitude is leaning towards uncertainty or doubt. Incorrect.
B is the best answer choice.

Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
Each answer choice needs to be carefully evaluated in light of the information presented in the passage.
A. Correct. The first paragraph mentions that “Basel II recommendations focused on establishing a minimum capital requirement for financial institutions in order to reduce risks” and the second paragraph mentions that “The Basel III accord primarily seeks to lower risk exposure by developing a consistent and transparent capital base and thus increasing banks’ liquidity. Basel III aims at ensuring that any losses that may arise are cushioned by high quality capital”; the passage states that both the Basel II and Basel III recommendations addressed risk by mandating the banks to create a reserve capital, but the Basel III accord focuses on having a high quality capital, whereas the Basel II recommendations focused on having a minimum capital; in other words, the Basel III accord differs from Basel II recommendations because it focuses on the quality of banks’ capital rather than on the amount of capital, as the answer choice mentions.
B. The first paragraph mentions that “Basel I regulations concentrated on categorizing borrowers with respect to their level of risks”; the passage makes no connection between defining risk levels and the Basel II recommendations; so, it is incorrect to infer that the Basel III accord differs from Basel II recommendations because it enhances the process of risk management rather than defines risk levels. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the Basel III accord focuses on having a “high quality capital”, whereas the Basel II recommendations focused on having a “minimum capital”. Incorrect.
C. The second paragraph mentions that “the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord. Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”; the passage suggests that the Basel III accord does not consider implementation aspects in developing countries; so, it is incorrect to infer that the Basel III accord differs from Basel II recommendations because it considers implementation aspects in developing countries rather than the developed countries. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the Basel III accord focuses on having a “high quality capital”, whereas the Basel II recommendations focused on having a “minimum capital”. Incorrect.
D. Trap. The second paragraph mentions that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management”; the Basel III accord, and not the Basel II recommendations, seeks to “widen the risk coverage”; so, it is incorrect to infer that the Basel III accord differs from Basel II recommendations because it controls the risk rather than widens the risk coverage. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the Basel III accord focuses on having a “high quality capital”, whereas the Basel II recommendations focused on having a “minimum capital”. Incorrect.
E. The first paragraph mentions that “Basel I regulations concentrated on categorizing borrowers with respect to their level of risks”; the passage makes no connection between categorizing buyers based on risk and the Basel II recommendations; so, it is incorrect to infer that the Basel III accord differs from Basel II recommendations because it seeks to lower the risk of the banks rather than categorize buyers based on risk. Furthermore, our expectation from the correct answer choice is on the lines that the Basel III accord focuses on having a “high quality capital”, whereas the Basel II recommendations focused on having a “minimum capital”. Incorrect.
A is the best answer choice.

Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
The second paragraph mentions that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord”; it can be inferred that the author feels positive about Basel III’s approach to risk management, but the author is also concerned about its practical implementation. The term “promising” is used to suggest “fundamental correctness”. Each answer choice needs to be carefully evaluated in light of the information presented in this context.
A. The second paragraph mentions that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord”; although it can be inferred that the author feels positive about Basel III’s approach to risk management, the passage doesn’t suggest that the author believes that the approach adequately addresses the concerns regarding banks’ risks. Furthermore, it can be inferred that the author feels positive about Basel III’s approach to risk management, but the author is also concerned about its practical implementation; so, the term “promising” is used to suggest “fundamental correctness”; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
B. The passage neither mentions the risk management approach of the banking sector regulators in most counties nor compares it with that of Basel III; the term “promising” is not used to suggest such a contrast. Furthermore, it can be inferred that the author feels positive about Basel III’s approach to risk management, but the author is also concerned about its practical implementation; so, the term “promising” is used to suggest “fundamental correctness”; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
C. Correct. The second paragraph mentions that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord”; it can be inferred that the author feels positive about Basel III’s approach to risk management, but the author is also concerned about its practical implementation; so, the term “promising” is used to suggest “fundamental correctness”; in other words, the author regards the Basel III accord’s approach to risk management as “promising” in order to show confidence in the theoretical soundness of the approach.
D. Trap. The second paragraph mentions that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord”; although the author raises questions over the successful implementation of risk management proposals, the term “promising” is not used to raise questions. Furthermore, it can be inferred that the author feels positive about Basel III’s approach to risk management, but the author is also concerned about its practical implementation; so, the term “promising” is used to suggest “fundamental correctness”; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
E. The second paragraph mentions that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord”; although it can be inferred that the author believes that risk management is important, the term “promising” is not used to make such an inference. Furthermore, it can be inferred that the author feels positive about Basel III’s approach to risk management, but the author is also concerned about its practical implementation; so, the term “promising” is used to suggest “fundamental correctness”; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Incorrect.
C is the best answer choice.

Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map
To explain why Basel II recommendations failed (Paragraph 1)
To mention Basel III’s approach and suggest that Basel III has challenges (Paragraph 2)
The second paragraph mentions three challenges – firstly, “this regulation may not sufficiently address issues associated with the capital ratios of financial institutions”, secondly, “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord. Most countries in the developing world have failed to implement most of its provisions as was witnessed with the previous recommendations”, and thirdly, “regulators and central banks in most countries have indicated that increasing the risk reserve may negatively affect the regular operation of their banks”. If an answer choice shows that any of these challenges can be overcome, that answer choice improves the likelihood of the Basel III accord achieving its goal.
A. If increasing the risk reserve was found to affect the operation of banks more negatively than previously believed, fear of “regulators and central banks in most countries” is confirmed, casting doubt on whether the Basel III accord will achieve its goal. Incorrect.
B. Trap. The second paragraph suggests that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord”; it can be inferred that forcing “banking sector regulators” is the challenge; so, if a new economic study showed that widening risk coverage is not the most efficient way of enhancing the process of risk management, it does not directly impact the success of the Basel III accord. Incorrect.
C. If issues associated with the capital ratios of banks worsened in a few months after implementing the Basel III recommendations, it confirms the belief that “this regulation may not sufficiently address issues associated with the capital ratios of financial institutions”, casting doubt on whether the Basel III accord will achieve its goal. Incorrect.
D. Trap. The second paragraph suggests that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord”; it can be inferred that forcing “banking sector regulators” is the challenge; so, if a few banks implementing the Basel III recommendations successfully widened their risk coverage, it does not suggest that the challenge related to forcing “banking sector regulators” is likely overcome. Moreover, because these are “a few banks”, it does not directly impact the overall success of the Basel III accord. Incorrect.
E. Correct. The second paragraph suggests that “The Basel III accord also seeks to widen the risk coverage as a way of enhancing the process of risk management. This is a promising approach, but the banking sector regulators must be forced to implement most of the risk management proposals covered under this accord”; it can be inferred that forcing “banking sector regulators” is the challenge; so, if banking regulators across the world enforced most of the risk management proposals under Basel III, it improves the likelihood of the Basel III accord achieving its goal.
E is the best answer choice.
Please find another set of GMAT-style RC questions with explanations on: How to Solve GMAT Reading Comprehension Prep
Please find another set of GMAT-style RC questions with explanations on: Free GMAT Reading Comprehensions Prep
Please find another set of GMAT-style RC questions with explanations on: Free GMAT Verbal Prep
Please find another set of GMAT-style RC questions with explanations on: Free GMAT Verbal Sample Questions
Please find another set of GMAT-style RC questions with explanations on: Free GMAT Sample Questions
GMAT Critical Reasoning checks how clearly you understand an argument and how confidently you can test its logic. In the Verbal section, you only see two question types: Reading Comprehension and Critical Reasoning. Out of 23 Verbal questions, you typically face about 8 to 10 Critical Reasoning questions. That puts close to 40 percent of Verbal in the Critical Reasoning zone, so it plays a major role in a strong GMAT score. Even better, your prep gives you a skill that travels far beyond the test. You learn to spot gaps, weigh evidence, and make decisions with clarity, which supports many other GMAT question types. It also shows up in business school, in management work, and in everyday choices. Think of Critical Reasoning prep as a powerful upgrade to the way you think, not just the way you test.

CR Assumption questions challenge you to find the unspoken idea that must hold true for the argument to make sense. They guide you to uncover the hidden connection between the premise and the conclusion.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Assumption concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Assumption Prep
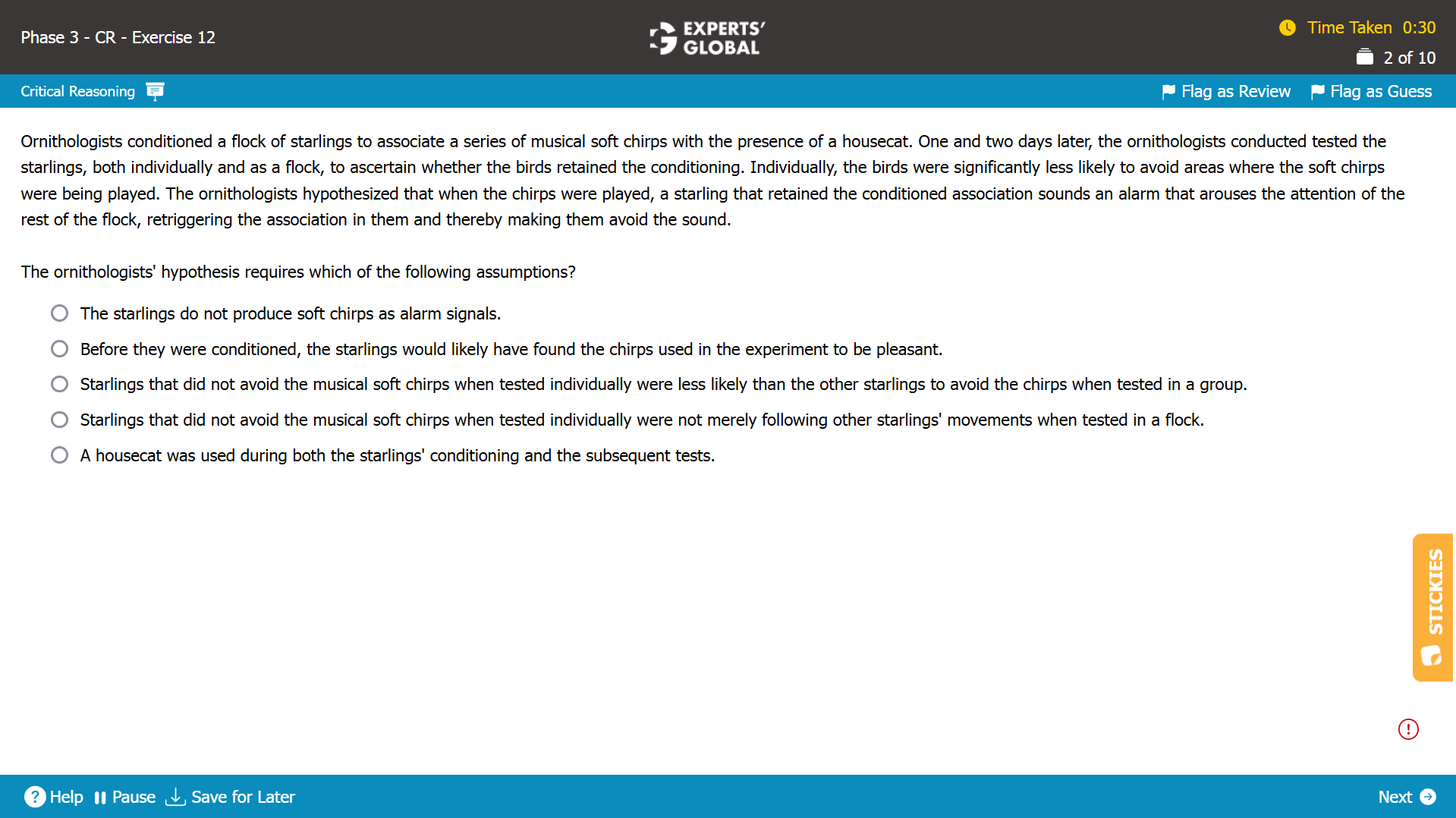
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map: Starlings conditioned to associate musical chirps with a housecat → testing to determine retention of conditioning → starlings avoided musical chirps more in flock than individually → a starling retaining the conditioning gives off an alarm to other starlings for them to avoid musical soft chirps (conclusion)
Missing-link: Between starlings avoiding musical chirps more in flock than individually and the conclusion that a starling retaining the conditioning gives off an alarm to other starlings for them to avoid musical soft chirps
Expectation from the correct answer choice: To strengthen the conclusion that a starling retaining the conditioning gives off an alarm to other starlings for them to avoid musical soft chirps, through a valid assumption
A. The argument is concerned with a starling giving off an alarm to other starlings, and not with the nature of the alarm; so, this answer choice simply adds detail and has no bearing on the reasoning or its conclusion. Besides, this condition is not necessary for the argument to hold and thus, is not a valid assumption. Because this answer choice does not strengthen the conclusion through a valid assumption, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. Whether the starlings would likely have found the chirps used in the experiment to be pleasant has no bearing on the argument or its conclusion. Besides, this condition is not necessary for the argument to hold and thus, is not a valid assumption. Because this answer choice does not strengthen the conclusion through a valid assumption, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. Trap. By suggesting that the starlings that did not retain the conditioning were “less likely than others” to avoid musical chirps in a flock, this answer choice contradicts the argument’s suggestion that once a starling gives off an alarm to other starlings, all starlings were “equally likely” to avoid musical chirps (and more likely than they would be in individual testing). Because this answer choice does not strengthen the conclusion through a valid assumption, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. Correct. By suggesting that the starlings that did not retain the conditioning were not merely following other starlings’ movements in a group test, this answer choice strengthens the conclusion that, in a flock, a starling retaining the conditioning gives off an alarm to other starlings for them to avoid musical soft chirps. Additionally, this statement does have to be true for the conclusion to hold; negating this statement would mean that “starlings that did not avoid the musical soft chirps when tested individually were merely following other starlings’ movements when tested in a flock”; such a suggestion casts doubt on one starling giving off an alarm to other starlings and thus, negates the conclusion. Because this answer choice strengthens the conclusion through a valid assumption, this answer choice is correct.
E. The use of a housecat in the later tests casts doubt regarding whether it was the housecat or the alarm by a fellow starling that made the starlings avoid musical chirps in a flock test; so, this answer choice, if anything, weakens, rather than strengthens, the argument. Because this answer choice does not strengthen the conclusion through a valid assumption, this answer choice is incorrect.
D is the best choice.
Strengthen the Argument questions in GMAT Critical Reasoning present an argument, and your task is to select the answer choice that strengthens it. You need to choose the option that fills the missing link between the information provided and the conclusion drawn.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Strengthen the Argument concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Strengthen the Argument Prep
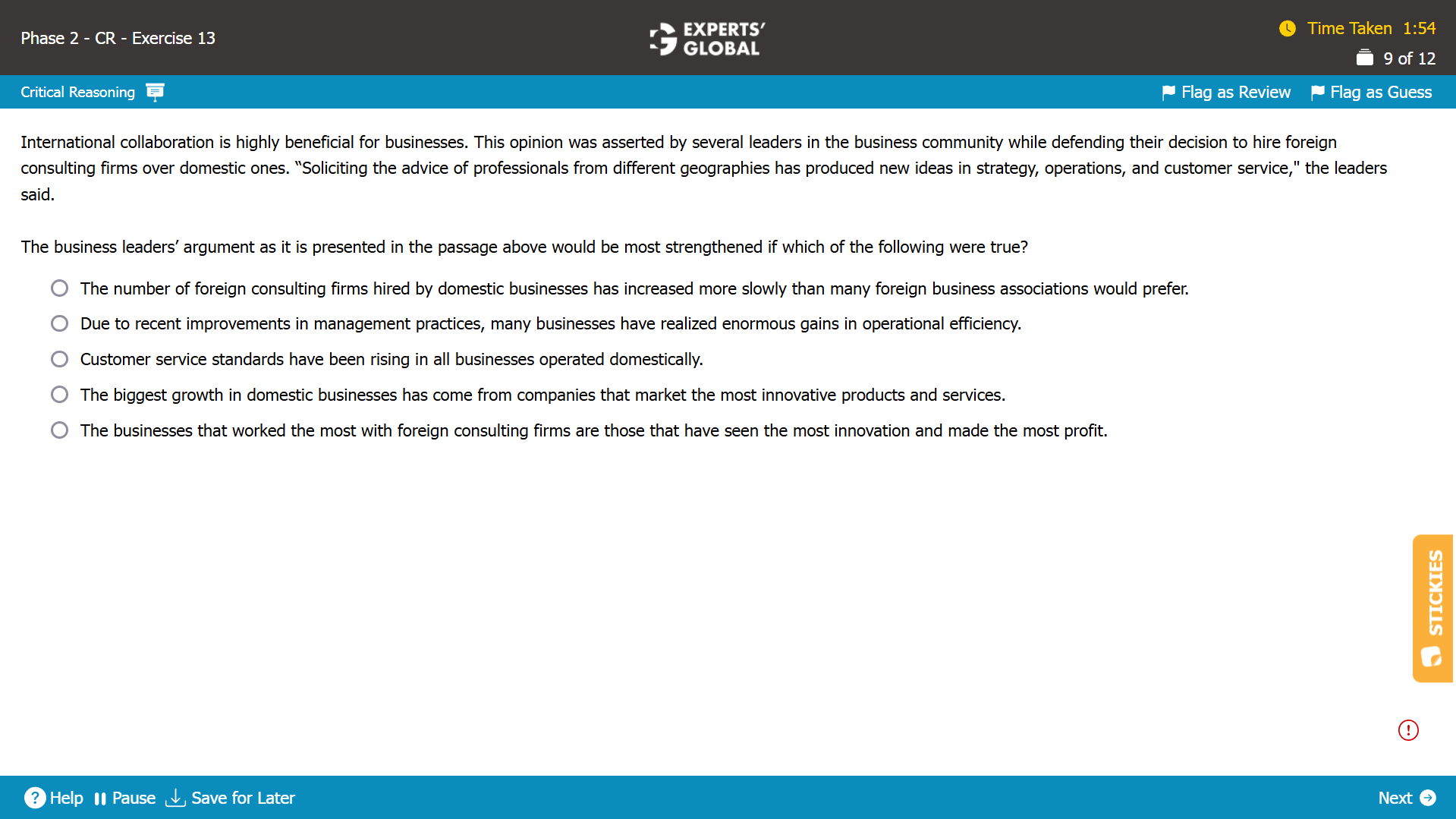
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map: International collaboration is beneficial for businesses → advice of professionals from different geographies has produced business benefits → hiring foreign consulting firms over domestic ones is beneficial to businesses (implicit conclusion)
Missing-link: Between the advice of professionals from different geographies producing business benefits and the conclusion that hiring foreign consulting firms over domestic ones is beneficial to businesses
Expectation from the correct answer choice: To strengthen the conclusion that hiring foreign consulting firms over domestic ones is beneficial to businesses
A. This answer choice, suggesting an increase in the hiring of foreign consulting firms, provides no information about the impact of hiring foreign firms; so, this answer choice simply adds information, which, although relevant to the broad context of the argument, does not strengthen the conclusion. Because this answer choice does not strengthen the conclusion, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. This answer choice, citing business benefits because of improvement in management practices, provides no information about whether the improvement/business benefits were caused by hiring foreign consulting firms; so, this answer choice simply adds information, which, although relevant to the broad context of the argument, does not strengthen the conclusion. Because this answer choice does not strengthen the conclusion, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. This answer choice, citing a rise in all customer service standards in all domestic businesses, provides no information about whether this rise was related to hiring foreign consulting firms; so, this answer choice simply adds information, which, although relevant to the broad context of the argument, does not strengthen the conclusion. Because this answer choice does not strengthen the conclusion, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. This answer choice, suggesting that marketing innovative products and services brings business growth, provides no information about the role of foreign consulting firms; so, this answer choice simply adds information, which, although relevant to the broad context of the argument, does not strengthen the conclusion. Because this answer choice does not strengthen the conclusion, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. Correct. By establishing a correlation between hiring foreign consulting firms and businesses being most innovative and most profitable, this answer choice hints at the possibility that hiring foreign consulting firms may have caused these business benefits, thus strengthening the conclusion. Because this answer choice strengthens the conclusion, this answer choice is correct.
E is the best choice.
CR Weaken the Argument questions, or simply weakening questions, ask you to identify the statement that weakens an argument by challenging the missing link between the premise and the conclusion.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Weaken the Argument concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Weaken the Argument Prep
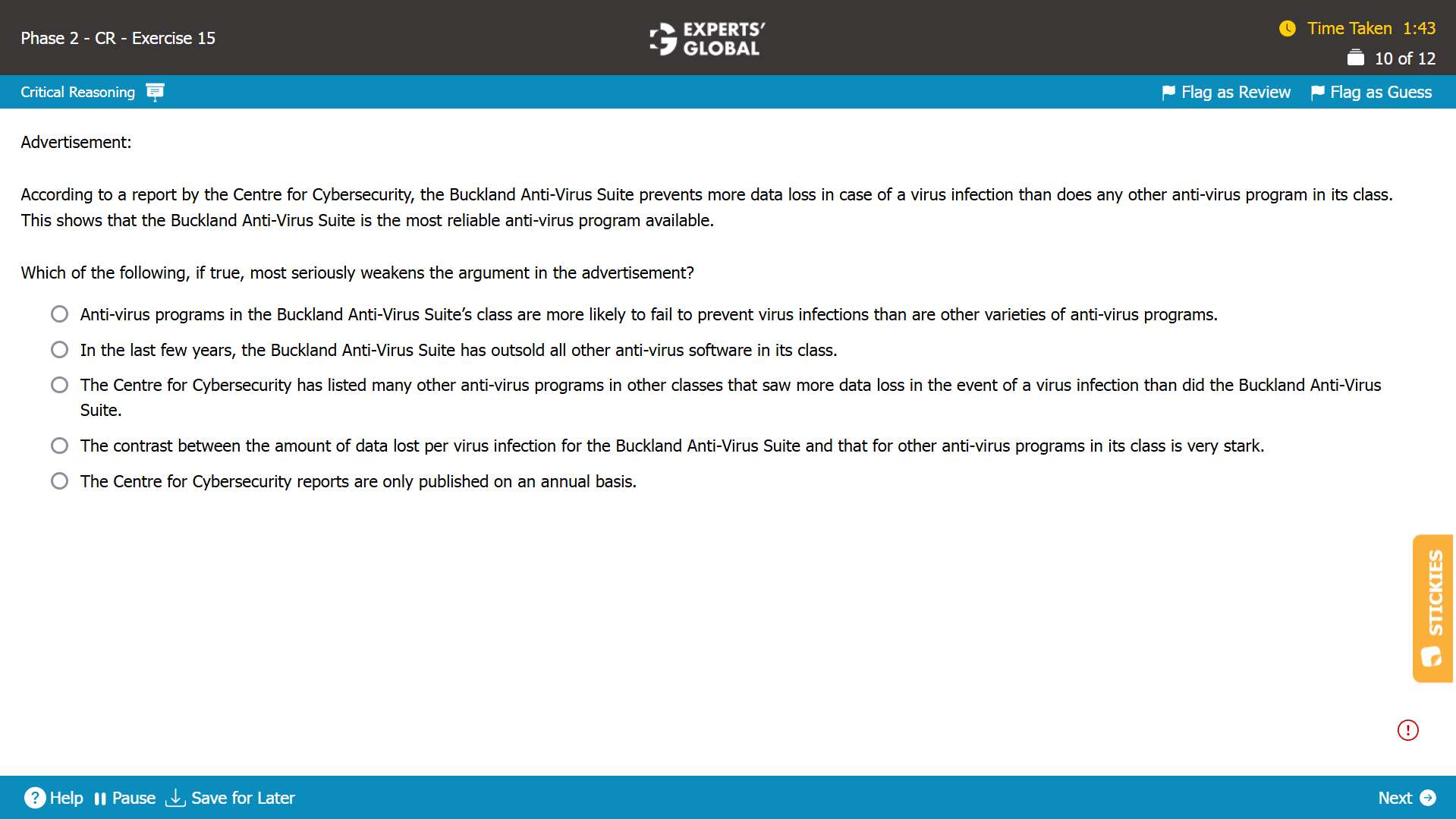
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map: Buckland anti-virus prevents more data loss in case of virus infection than other similar programs in its class → Buckland anti-virus is the most reliable anti-virus program available (conclusion)
Missing-link: Between Buckland anti-virus preventing more data loss in case of virus infection than other similar programs in its class and the conclusion that Buckland anti-virus is the most reliable anti-virus program available
Expectation from the correct answer choice: To weaken the conclusion that Buckland anti-virus is the most reliable anti-virus program available
A. Correct. By suggesting that Buckland anti-virus belongs to a class that is more likely to fail to prevent virus infections in the first place than other classes, this answer choice indicates that anti-virus programs in this class are not likely to be the “most” reliable; in other words, Buckland anti-virus, regardless of its superior performance “within” its class in preventing data loss in case of virus infection, is not likely the most reliable anti-virus program overall; please note that the conclusion is about “all anti-virus programs available across all classes” and not only the programs “in a particular class”; so, this answer choice weakens the conclusion. Because this answer choice weakens the conclusion, this answer choice is correct.
B. Trap. This answer choice, suggesting that the Buckland anti-virus has “outsold” other anti-virus programs in its class, provides no information about whether the Buckland anti-virus is the “most reliable” option; it is possible that it outsold its competitors because of another reason, such as cost or availability, other than reliability; so, this answer choice is just additional information and does not weaken the argument. Because this answer choice does not weaken the conclusion, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. This answer choice, suggesting that there are many other anti-virus programs in other classes that are not as effective as Buckland’s anti-virus in preventing data loss, simply indicates that Buckland’s anti-virus is “more” reliable than “many” other options available; the answer choice does not address whether Buckland’s anti-virus is the “most” reliable among “all” programs available; overall, this answer choice, if anything, faintly strengthens, rather than weakens, the conclusion. Because this answer choice does not weaken the conclusion, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. Trap. The argument mentions that Buckland anti-virus prevents “more” data loss in case of virus infection than other similar anti-virus programs in its class; so, this answer choice, suggesting that the difference in the amount of data lost is “very stark”, is just additional detail and does not weaken the argument. Because this answer choice does not weaken the conclusion, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. Trap. The argument is concerned with the reliability of the Buckland anti-virus, as per information cited in a report; so, the frequency of the report is just additional information and has no bearing on the argument. Because this answer choice does not weaken the conclusion, this answer choice is incorrect.
A is the best choice.
Resolve the Paradox questions in GMAT Critical Reasoning present an argument where the conclusion appears to be in contrast with the information provided. Your task is to select the answer choice that provides a logical explanation for this discrepancy.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Resolve-the-Paradox concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Resolve-the-Paradox Prep
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
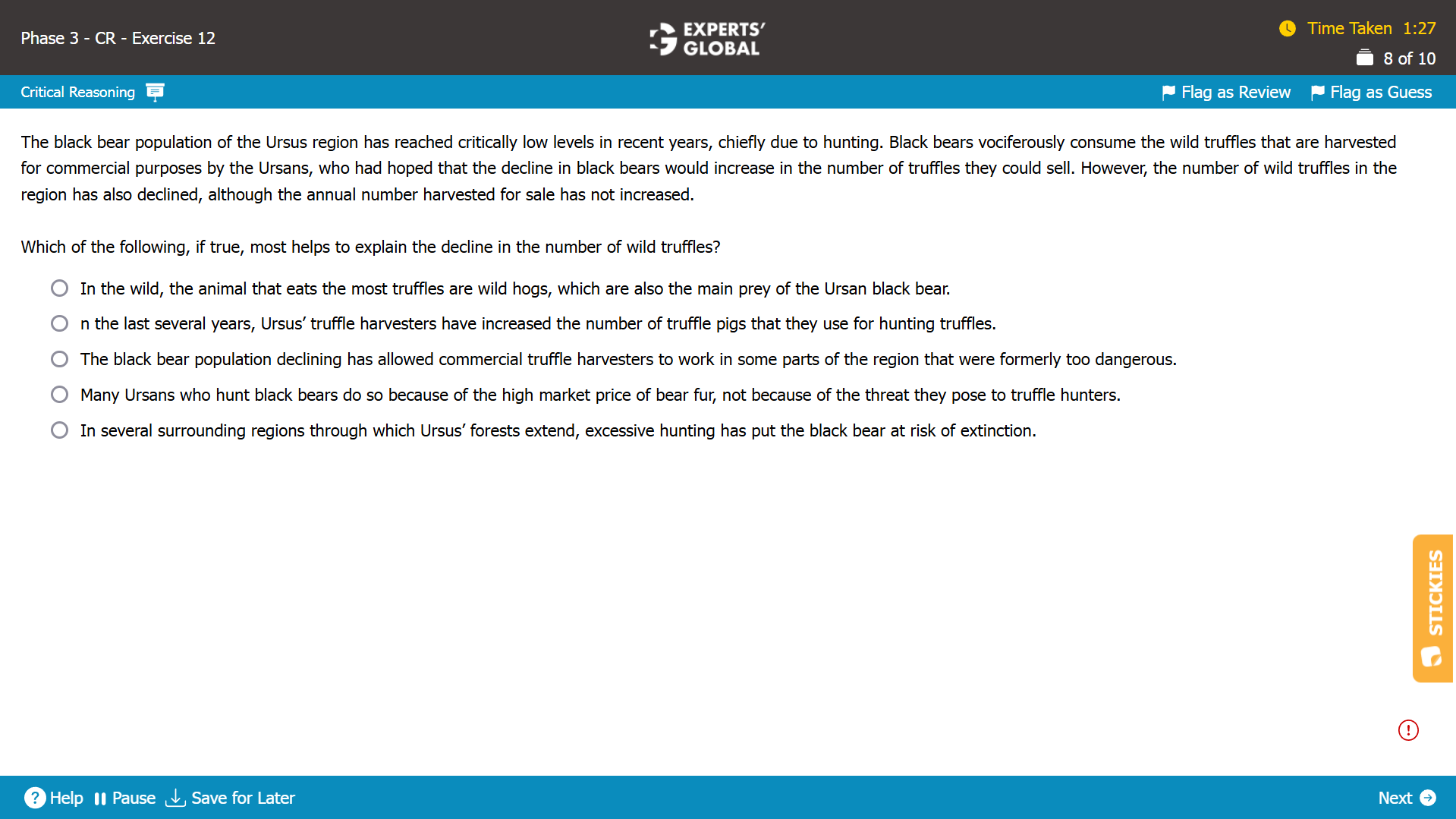
Mind-map: Black bear population reached low levels due to hunting → bears consume truffles → decline in bear population expected to increase number of truffles → number of truffles harvested did not increase → number of wild truffles declined
Missing-link: Between bear population declining but the number of truffles harvested not increasing and number of wild truffles declining
Expectation from the correct answer choice: To explain why the number of wild truffles declined despite the bear population declining and despite the number of truffles harvested not increasing
A. Correct. By suggesting that the wild hogs that feed on most truffles are the main prey of the bear, this answer choice indicates that the decline in bear populations likely led to an increase in the population of wild hogs who likely consumed more truffles than before, leading to a decline in truffles population; thus, this answer choice explains why the number of wild truffles declined despite the bear population declining and despite the number of truffles harvested not increasing. Because this answer choice clarifies the exact discrepancy, this answer choice is correct.
B. Trap. If there is an increase in the number of truffle pigs used for hunting truffles, it indicates a likely increase in truffle harvesting activity; however, the argument mentions that the annual number of truffles harvested for sale has not increased, suggesting that even if greater truffle harvesting took place in new areas, the greater activity has no bearing on the argument. Because this answer choice does not explain the discrepancy in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. Trap. If the decline in bear populations facilitated commercial truffle harvesting in previously dangerous areas, it indicates that commercial truffle harvesting took place in new areas; however, the argument mentions that the annual number of truffles harvested for sale has not increased, suggesting that even if commercial truffle harvesting took place in new areas, the new harvesting activity has no bearing on the argument. Because this answer choice does not explain the discrepancy in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. Trap. The argument is concerned with why the number of wild truffles declined despite the bear population declining; so, information about the reason for bear hunting is just additional information and does not explain the discrepancy in the argument. Because this answer choice does not explain the discrepancy in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. The argument is concerned with why the number of wild truffles declined despite the bear population declining; so, whether the decline increases the bear species’ risk of extinction is out of scope and does not explain the discrepancy in the argument. Because this answer choice does not explain the discrepancy in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
A is the best choice.
GMAT Critical Reasoning Evaluate the Argument questions ask you to find the information that lets you assess the strength of an argument by determining if its reasoning stands strong or falls apart.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Evaluate-the-Argument concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Evaluate-the-Argument Prep
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
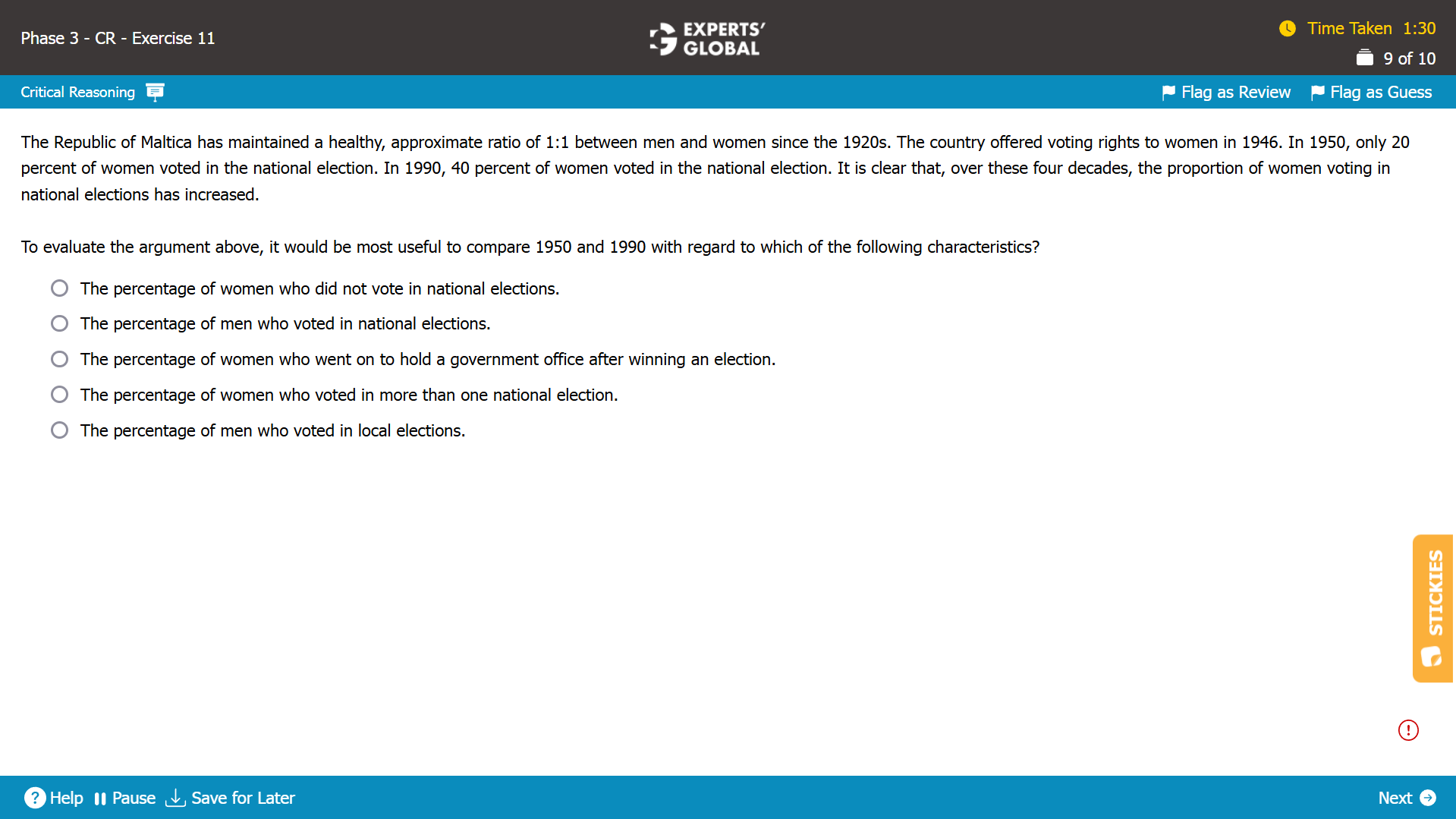
Mind-map: In 1950 election, 20 percent women voted → in 1990 election, 40 percent women voted → proportion of women voting in elections has increased (conclusion)
Missing-link: Between all the information presented and the conclusion that the proportion of women voting in elections has increased
Expectation from the correct answer choice: To find the information that helps evaluate the conclusion that the proportion of immigrants in voting has increased
Discussion: This question tests the classic GMAT error of getting impressed by numbers, or assuming that the stated numbers indicate something positive/desirable or negative/undesirable; the argument mentions that in 1950, among all women, 20 percent of women voted and that in 1990, among all women, 40 percent of women voted; the increase from 20 percent to 40 percent generates the impression of more women voting; this increase in women’s voting indicates the increase in women voters, among all women, and not the increase in women voters, among all voters. Additionally, the conclusion relates to the proportion of women voters among all voters; to evaluate this conclusion, it is necessary to know the proportion of men voters among all voters. Besides, please be extra careful when you see numbers/percentages/proportions in CR questions; often, the key lies in the numbers.
A. The argument mentions the percentage of women who voted in the two years, suggesting that the comparison of the percentage of women who did not vote in the two years is already known; so, this answer choice seeks no new information and does not seek the information that helps evaluate the conclusion. Further, this answer choice relates to information about “women” and fails to address the comparison between women and men, thus not leading to any suggestion related to the “proportion” of women, among all voters. Because this answer choice does not seek the required information, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. Correct. The argument mentions that, over time, the proportion of women voting in elections, among all voters, has increased because a greater percentage of women, among all women, are voting; the term “proportion”, as used in the conclusion, indicates the ratio of women voters and all voters; to know the proportion of women voters among all voters, the proportion of men voters among all voters is necessary; if there is a similar or greater increase in the percentage of men voters, the “proportion” of women voters, among all voters, may remain the same or decrease, despite the increase in the “percentage” of women, among all women, voting; so, information about the percentage of men who voted in national elections, as the answer choice mentions, is essential to evaluate the argument. Because this answer choice seeks the required information, this answer choice is correct.
C. The argument is concerned with the women “who voted in national elections” and not with those “who went on to hold a government office after winning an election”; so, the response to this answer choice would be out of scope. Further, this answer choice relates to information about “women” and fails to address the comparison between women and men, thus not leading to any suggestion related to the “proportion” of women, among all voters. Because this answer choice does not seek the required information, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. The argument is concerned with the women “who voted in national elections” and whether they voted in more than one election would be just additional information and have no bearing on the argument. Further, this answer choice relates to information about “women” and fails to address the comparison between women and men, thus not leading to any suggestion related to the “proportion” of women, among all voters. Because this answer choice does not seek the required information, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. This answer choice is concerned with “national” elections; so, “local” elections are out of scope. Because this answer choice does not seek the required information, this answer choice is incorrect.
B is the best choice.Mind-map: Black bear population reached low levels due to hunting → bears consume truffles → decline in bear population expected to increase number of truffles → number of truffles harvested did not increase → number of wild truffles declined
Missing-link: Between bear population declining but the number of truffles harvested not increasing and number of wild truffles declining
Expectation from the correct answer choice: To explain why the number of wild truffles declined despite the bear population declining and despite the number of truffles harvested not increasing
A. Correct. By suggesting that the wild hogs that feed on most truffles are the main prey of the bear, this answer choice indicates that the decline in bear populations likely led to an increase in the population of wild hogs who likely consumed more truffles than before, leading to a decline in truffles population; thus, this answer choice explains why the number of wild truffles declined despite the bear population declining and despite the number of truffles harvested not increasing. Because this answer choice clarifies the exact discrepancy, this answer choice is correct.
B. Trap. If there is an increase in the number of truffle pigs used for hunting truffles, it indicates a likely increase in truffle harvesting activity; however, the argument mentions that the annual number of truffles harvested for sale has not increased, suggesting that even if greater truffle harvesting took place in new areas, the greater activity has no bearing on the argument. Because this answer choice does not explain the discrepancy in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. Trap. If the decline in bear populations facilitated commercial truffle harvesting in previously dangerous areas, it indicates that commercial truffle harvesting took place in new areas; however, the argument mentions that the annual number of truffles harvested for sale has not increased, suggesting that even if commercial truffle harvesting took place in new areas, the new harvesting activity has no bearing on the argument. Because this answer choice does not explain the discrepancy in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. Trap. The argument is concerned with why the number of wild truffles declined despite the bear population declining; so, information about the reason for bear hunting is just additional information and does not explain the discrepancy in the argument. Because this answer choice does not explain the discrepancy in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. The argument is concerned with why the number of wild truffles declined despite the bear population declining; so, whether the decline increases the bear species’ risk of extinction is out of scope and does not explain the discrepancy in the argument. Because this answer choice does not explain the discrepancy in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
A is the best choice.
Critical Reasoning Inference questions challenge you to find a statement that must be true based on the information provided, without any assumption or overstatements.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Inference Questions concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Inference Questions Prep
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
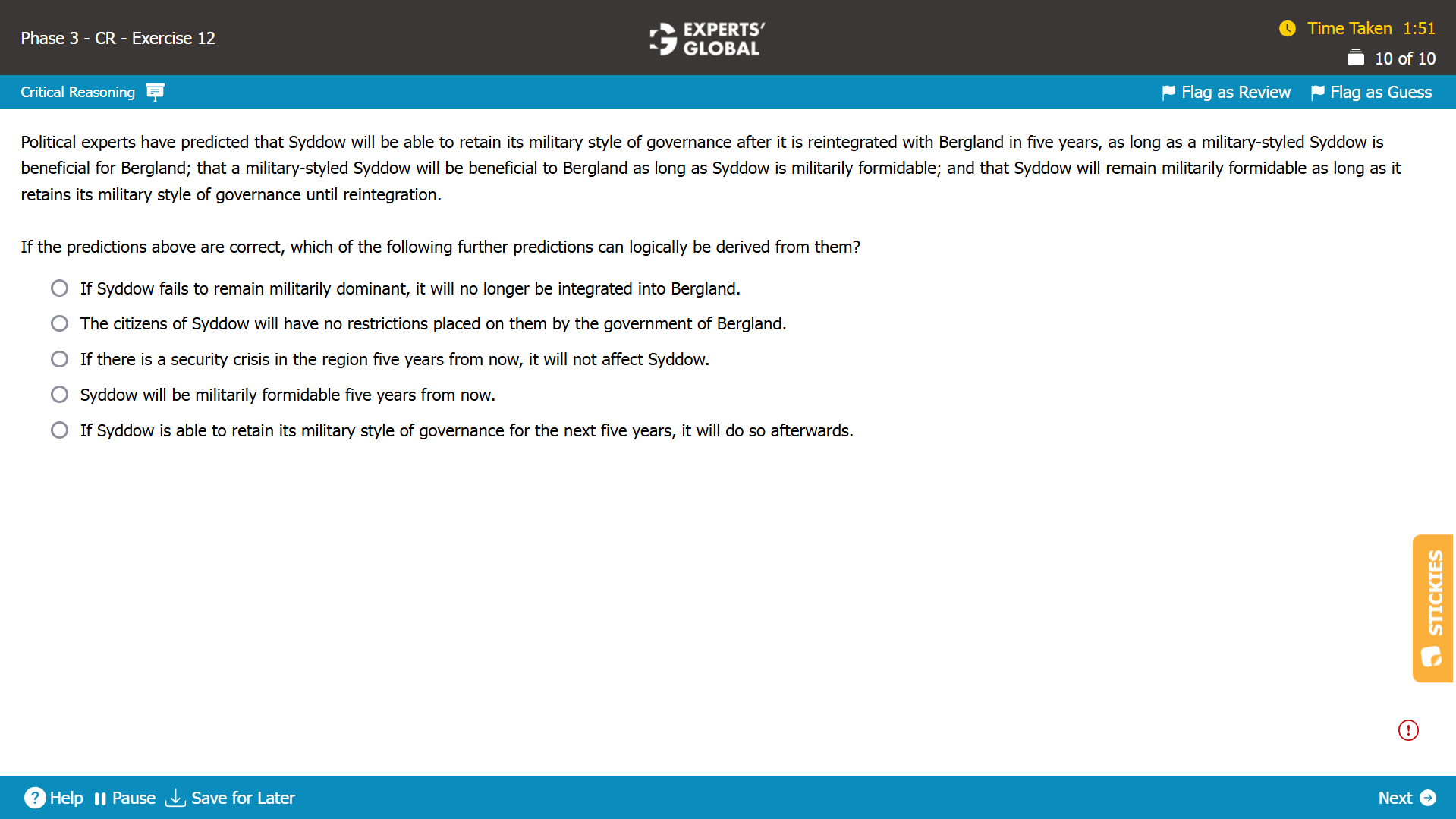
Mind-map: Syddow will reintegrate with Bergland → if Syddow retains military style of governance until reintegration → Syddow will be militarily formidable → Syddow will be beneficial for Bergland → Syddow will retain its military style of governance
Missing-link: Not needed
Expectation from the correct answer choice: To be duly deducible from the information in the passage, without any assumption or extrapolation
A. Trap. The argument mentions that Syddow will be beneficial to Bergland as long as Syddow is militarily formidable; so, it can be inferred that if Syddow fails to remain militarily dominant, it will not be beneficial to Bergland; however, the passage makes no suggestion that Syddow’s reintegration is dependent on whether Syddow remains militarily dominant; so, this answer choice, suggesting such a condition, cannot be established. Because this answer choice is not deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. The argument makes no suggestion regarding the Bergland government’s restriction on Syddow citizens; so, this answer choice, suggesting such restrictions, is just a possibility, which, although relevant to the broad context of the argument, cannot be established. Because this answer choice is not deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. Whether a security crisis affects Syddow depends on whether Syddow is militarily formidable; the argument mentions that whether Syddow is militarily formidable depends on whether Syddow retains a military style of governance; so, whether a security crisis affects Syddow is conditional and it cannot be inferred that a security crisis will not affect Syddow. Because this answer choice is not deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. Trap. The argument mentions that whether Syddow is militarily formidable depends on whether Syddow retains a military style of governance; so, whether Syddow will be militarily formidable five years from now is conditional and cannot be established. Because this answer choice is not deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. Correct. The argument mentions that if Syddow retains its military style of governance for the next five years, it will be militarily formidable and thus beneficial to Bergland, which will allow Syddow to retain its military style of governance; in other words, if Syddow retains its military style of governance for the next five years, it will be able to do so afterwards, as the answer choice mentions. Because this answer choice is deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is correct.
E is the best choice.
Critical Reasoning Main Point or Conclusion questions ask you to find the key idea the argument is trying to prove, the one point that all other details in the passage are designed to support.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Main Point or Conclusion concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Main Point or Conclusion Prep
Show Explanation
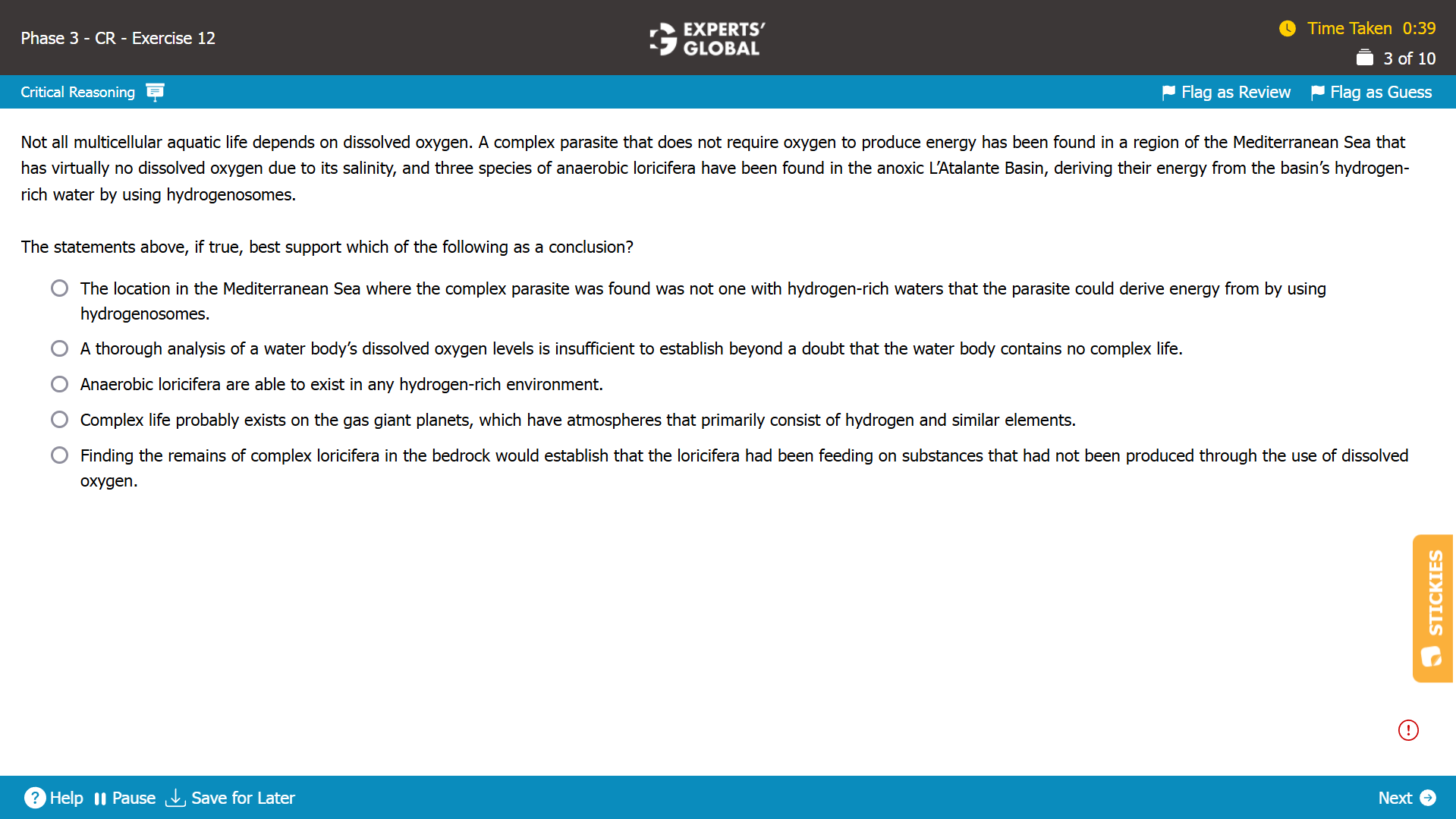
Mind-map: Not all multicellular aquatic life depend on dissolved oxygen → two complex aquatic organisms were found in waters that have no dissolved oxygen
Missing-link: Not needed
Expectation from the correct answer choice: To be duly deducible from the information in the passage, without any assumption or extrapolation
A. The argument mentions two complex aquatic organisms that were found in waters that have no dissolved oxygen – one is a complex parasite and the other are three species of anaerobic loricifera that use hydrogenosomes to derive energy; however, the argument makes no suggestion regarding the parasite’s ability to use hydrogenosomes to derive energy; so, this answer choice cannot be established. Because this answer choice is not deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. Correct. The argument mentions that not all multicellular aquatic life depend on dissolved oxygen and supports the claim by mentioning two organisms that were found in waters that have no dissolved oxygen; so, it can be established that a water body with no dissolved oxygen can have a complex life, or, in other words, a thorough analysis of a water body’s dissolved oxygen levels is insufficient to establish beyond a doubt that the water body contains no complex life, as the answer choice mentions. Because this answer choice is deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is correct.
C. The argument mentions that three species of anaerobic loricifera exist in “hydrogen-rich water” but makes no suggestion regarding whether anaerobic loricifera, in general, are able to exist in “any hydrogen-rich environment”; so, this answer choice cannot be established. Further, please note, a hint here is in the term “any”, which is extremely strong; one needs to be cautious of such answer choices as they are generally incorrect on the GMAT. Because this answer choice is not deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. This answer choice commits the classic GMAT error of extrapolation – the idea of reaching a conclusion for one set on the basis of observations on another set; the argument is concerned with multicellular “aquatic” life and its dependence on “dissolved” oxygen but provides no information about “life on gas giant planets”; so, this answer choice cannot be established. Because this answer choice is not deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. Trap. The argument mentions that three species of anaerobic loricifera do not require dissolved oxygen to survive, suggesting that the remains of these loricifera may not show any evidence of having fed on substances produced through dissolved oxygen; however, it cannot be established that the loricifera did not feed on such substances; in other words, it cannot be established that finding the remains of complex loricifera would establish that the loricifera had been feeding on substances that “had not been produced through the use of dissolved oxygen”, as the answer choice mentions. Because this answer choice is not deducible from the information in the passage without any assumption or extrapolation, this answer choice is incorrect.
B is the best choice.
CR Complete the Paragraph questions ask you to choose the answer that best follows the author’s reasoning, making sure the paragraph wraps up in a smooth and logical way.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Complete the Paragraph concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Complete the Paragraph Prep
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
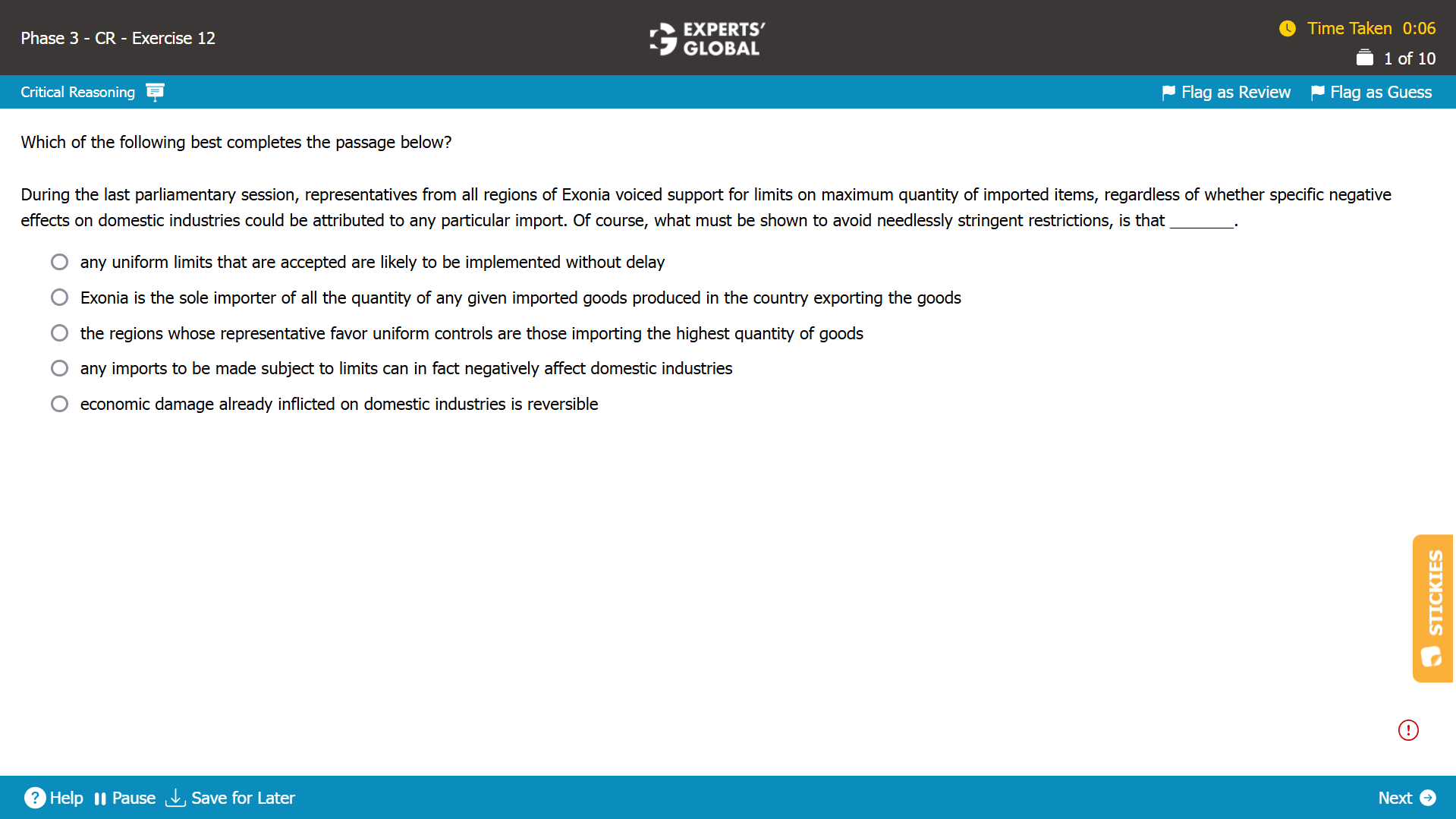
Mind-map: All representatives support uniform limits on imported items → even if a particular import has no specific effect on domestic industries → to avoid unnecessary restrictions, it must be shown that _____
Missing-link: Not needed
Expectation from the correct answer choice: Something on the lines of a provision that prevents excessive limits on imported items that have no negative impact domestically
A. This answer choice, suggesting that the limits would be implemented without a delay, indicates promptness in the implementation of the restrictions but makes no suggestion regarding how unnecessary restrictions would be avoided. Because this answer choice does not effectively complete the chain of thoughts developed in the passage, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. Trap. If Exonia imports all the goods of a particular type that the country exporting the goods produced, it indicates that controlling the maximum quantity of import is likely to reduce the exporting country’s export but makes no suggestion regarding how uniform limits prevent unnecessary restrictions on imported items that have no negative impact domestically. Because this answer choice does not effectively complete the chain of thoughts developed in the passage, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. Trap. This answer choice, suggesting that some representatives favor uniform limits, makes no suggestion regarding how unnecessary restrictions would be avoided. Besides, if a region imports the highest quantity of goods, the region’s representatives are not likely to favor any limits on the maximum quantity of imported items, thus contradicting the fact in the argument that representatives from “all” regions supported limits on maximum quantity of imported items. Because this answer choice does not effectively complete the chain of thoughts developed in the passage, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. Correct. If the possibility of negative effects of an import on domestic industries is judged before the import is made subject to limits, it indicates that only the imports that can negatively impact domestic industries would be likely subject to necessary restrictions, thus likely avoiding unnecessary restrictions on imports that are not harmful for domestic industries. Because this answer choice effectively completes the chain of thoughts developed in the passage, this answer choice is correct.
E. Regardless of whether economic damage already suffered by domestic industries is reversible, there is likely a need to limit imports to avoid future damage to domestic industries; however, any judgment on the reversibility of damage is just additional consideration and makes no suggestion regarding how unnecessary restrictions would be avoided. Because this answer choice does not effectively complete the chain of thoughts developed in the passage, this answer choice is incorrect.
D is the best choice.
GMAT Critical Reasoning Boldface questions present a paragraph with one or two boldfaced portions. Your task is to identify the role these boldfaced sections play in the argument.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Boldface concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Boldface Prep
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Strategy: Determining the main conclusion of the argument and finding the relation of the boldfaced portions with this conclusion
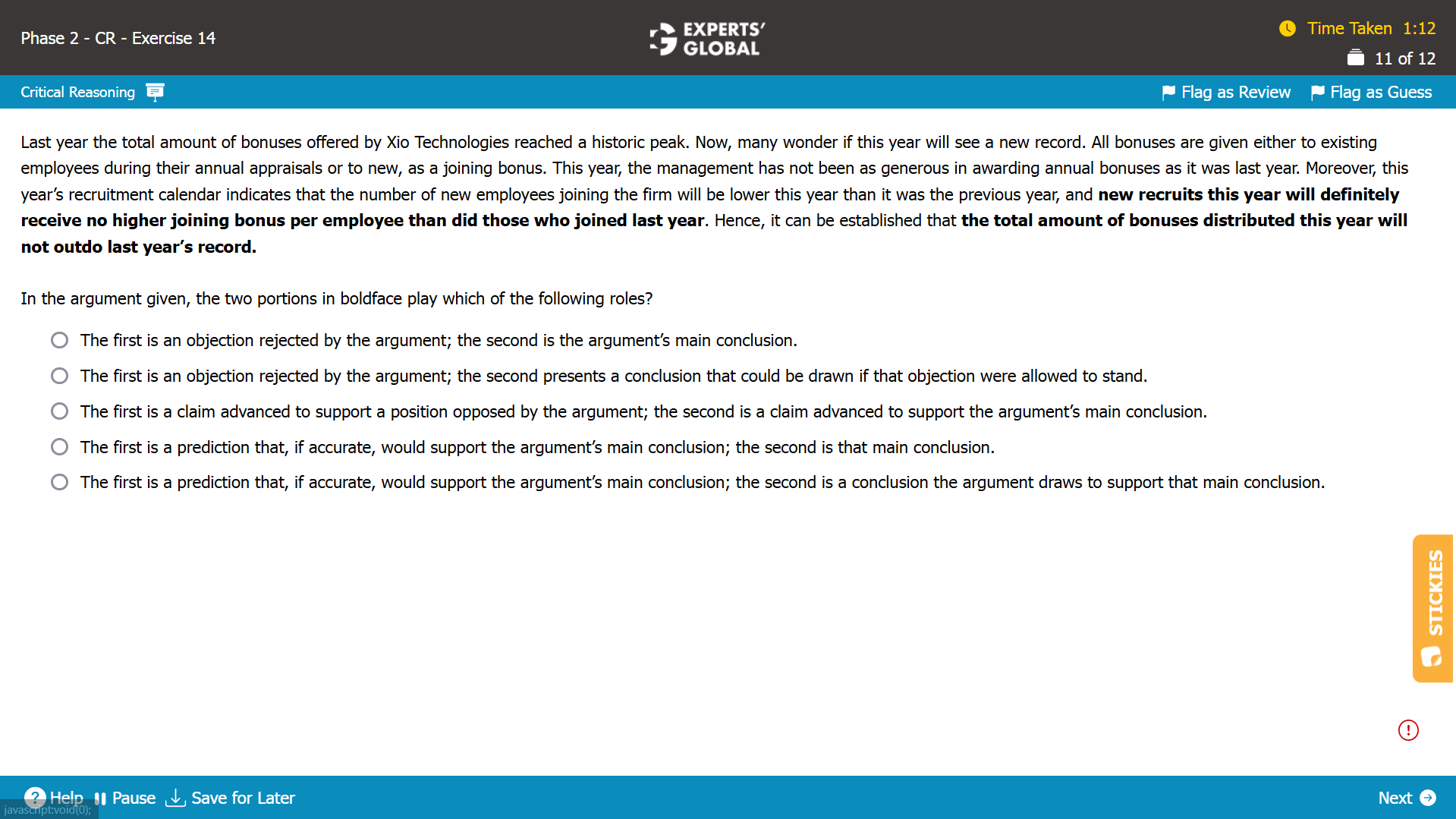
Logic: The argument explores the possibility of a company outdoing its previous year’s record of the total amount of bonuses offered in a year. The argument mentions that there are two ways in which bonuses are generally given – to existing employees as appraisal bonus and to new employees as joining bonus. The argument observes that the bonuses to existing employees this year will be lower than those last year and the number of new employees joining will likely not exceed that last year. The argument subsequently mentions, as the first boldface states, that new employees this year will not receive a higher joining bonus per employee than last year’s new employees did. Based on these considerations, the argument concludes in the second boldface that the total amount of bonuses offered this year will not outdo the last year’s record. In the context of the main conclusion – the first boldface is a judgment that the argument uses to establish the main conclusion; the second boldface is a prediction that the argument establishes as the main conclusion.
Main conclusion: The total amount of bonuses offered this year will not outdo the last year’s record.
Broad expectation from the correct answer choice:
The first boldface is a judgment that the argument uses to establish the main conclusion.
The second boldface is a prediction that the argument establishes as the main conclusion.
A.
Merit(s):
The first boldface disapproves the idea that new employees this year will receive a higher joining bonus per employee than last year’s new employees did; therefore, it is broadly correct to state that the first boldface is an “objection rejected by the argument”.
The second boldface is a prediction that the argument establishes as the main conclusion; therefore, it is correct to state that the second boldface is the “argument’s main conclusion”.
Demerit(s):
The first boldface is a judgment that the argument uses to establish the main conclusion, thus accepting the judgment; therefore, it is incorrect to state that the argument “rejects the first boldface”.
Because this answer choice does not correctly highlight the roles played by the two portions in boldface, this answer choice is incorrect.
B.
Merit(s):
The first boldface disapproves the idea that new employees this year will receive a higher joining bonus per employee than last year’s new employees did; therefore, it is broadly correct to state that the first boldface is an “objection rejected by the argument”.
The second boldface is a prediction that the argument establishes; therefore, it is correct to state that the second conclusion is a “conclusion”.
The first boldface is a judgment about an event in the future; the argument uses this judgment to establish the main conclusion in the second boldface; therefore, it is broadly correct to state that the “second boldface could be drawn if the first boldface were allowed to stand”.
Demerit(s):
The first boldface is a judgment that the argument uses to establish the main conclusion, thus accepting the judgment; therefore, it is incorrect to state that the argument “rejects the first boldface”.
Because this answer choice does not correctly highlight the roles played by the two portions in boldface, this answer choice is incorrect.
C.
Merit(s):
The first boldface is a judgment that the argument asserts to establish the main conclusion; therefore, it is broadly correct to state that the first boldface is a “claim”.
The second boldface is a prediction that the argument asserts; therefore, it is broadly correct to state that the second boldface is a “claim”.
Demerit(s):
The first boldface is a judgment that the argument uses to establish the main conclusion; so, the first boldface supports the argument’s position; therefore, it is incorrect to state that the first boldface “supports a position opposed by the argument”.
The second boldface itself is the main conclusion; therefore, it is incorrect to state that the second boldface “supports the argument’s main conclusion”.
Because this answer choice does not correctly highlight the roles played by the two portions in boldface, this answer choice is incorrect.
D.
Merit(s):
The first boldface is a judgment about an event in the future; therefore, it is correct to state that the first boldface is a “prediction”.
The argument uses the first boldface to establish the main conclusion; therefore, it is correct to state that the “first boldface, if accurate, would support the argument’s main conclusion”.
The second boldface is a prediction that the argument establishes as the main conclusion; therefore, it is correct to state that the second boldface is the “argument’s main conclusion”.
Demerit(s):
None
Because this answer choice correctly highlights the roles played by the two portions in boldface, this answer choice is correct.
E. Trap.
Merit(s):
The first boldface is a judgment about an event in the future; therefore, it is correct to state that the first boldface is a “prediction”.
The argument uses the first boldface to establish the main conclusion; therefore, it is correct to state that the “first boldface, if accurate, would support the argument’s main conclusion”.
The second boldface is a prediction that the argument establishes; therefore, it is correct to state that the second conclusion is a “conclusion”.
Demerit(s):
The second boldface itself is the main conclusion; therefore, it is incorrect to state that the second boldface “supports the argument’s main conclusion”.
Because this answer choice does not correctly highlight the roles played by the two portions in boldface, this answer choice is incorrect.
D is the best answer choice.
GMAT CR Method of Reasoning questions challenge you to spot the thinking pattern an argument follows, like how it makes conclusions, uses evidence, addresses counterarguments, or draws comparisons.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Method-of-Reasoning concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Method-of-Reasoning Prep
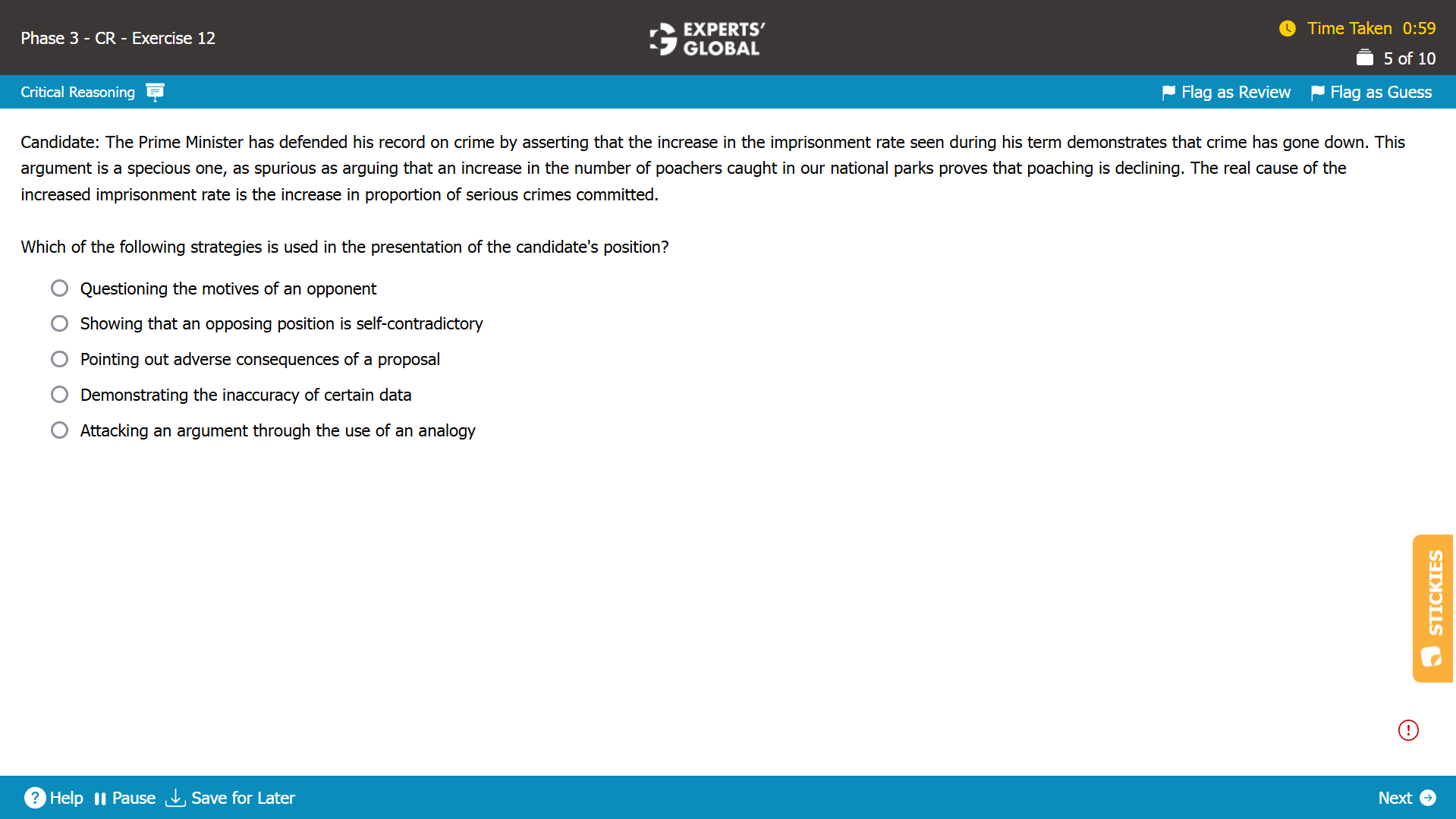
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map: Prime Minister: Imprisonment rate increased → crime went down → Candidate: misleading argument → more poachers caught does not indicate that poaching is declining → imprisonment rate increased because the proportion of serious crimes increased
Missing-link: Not needed
Expectation from the correct answer choice: Between the candidate showing the flaw in the Prime Minister’s argument by offering an analogy and by presenting an alternative explanation
A. The passage makes no suggestion that the candidate questions the “motives” of the Prime Minister; the candidate simply shows the flaw in the Prime Minister’s argument by offering an analogy and by presenting an alternative explanation. Further, “questioning the motives” indicates an emotional as well as unethical/crafty/manipulative tone; one needs to be cautious of such answer choices as they are generally incorrect on the GMAT. Because this answer choice does not indicate the strategy used in the candidate’s position, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. Trap. The term “self-contradictory” suggests the use of two views that oppose each other; the passage makes no suggestion that the candidate shows such a contradiction in the Prime Minister’s statement; the candidate simply shows the flaw in the Prime Minister’s argument by offering an analogy and by presenting an alternative explanation. Because this answer choice does not indicate the strategy used in the candidate’s position, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. Trap. The passage mentions the Prime Minister’s “claim” that crime has gone down in his tenure but makes no mention of the Prime Minister’s “proposal” or of the candidate pointing to a “consequence” of the Prime Minister’s statement; the candidate simply shows the flaw in the Prime Minister’s argument by offering an analogy and by presenting an alternative explanation. Because this answer choice does not indicate the strategy used in the candidate’s position, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. The passage makes no suggestion that the candidate questions the “accuracy” of the Prime Minister’s statement and demonstrates the same; the candidate simply shows the flaw in the Prime Minister’s argument by offering an analogy and by presenting an alternative explanation. Because this answer choice does not indicate the strategy used in the candidate’s position, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. Correct. The Prime Minister reasons that more criminals imprisoned suggests that crime is declining; to this reasoning, the candidate responds by suggesting that more poachers caught does not indicate that poaching is declining, thus indicating the flaw in the Prime Minister’s reasoning; in other words, the candidate establishes his position by attacking an argument through the use of an analogy, as the answer choice mentions. Because this answer choice indicates the strategy used in the candidate’s position, this answer choice is correct.
E is the best choice.
Logical Fallacy Critical Reasoning questions on the GMAT appear in familiar formats such as strengthen, weaken, resolve the paradox etc. The key skill in solving these questions is identifying the logical fallacy in the argument.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Logical Fallacy concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Logical Fallacy Prep
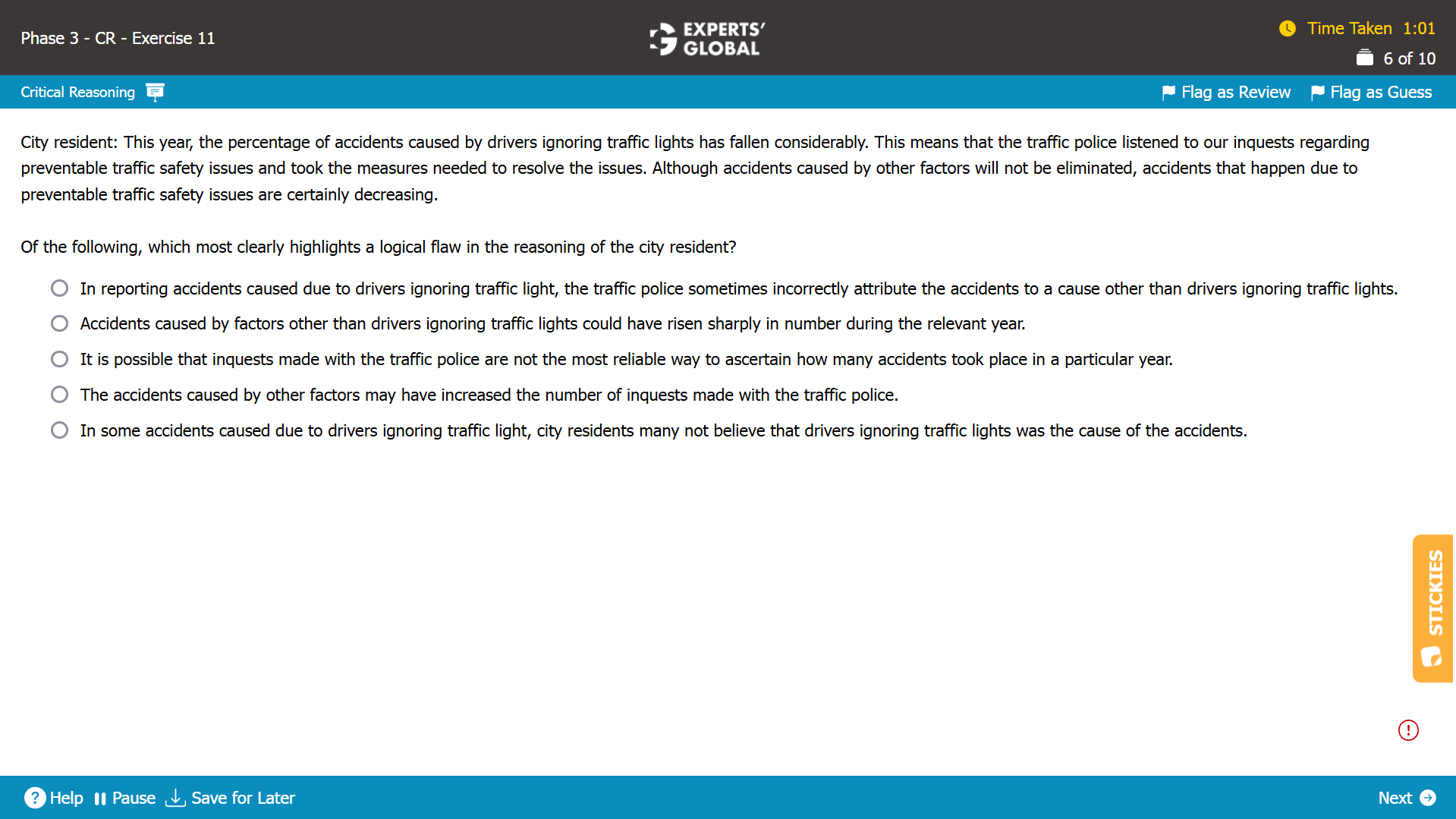
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map: Percentage of accidents caused by drivers ignoring traffic lights declined this year →resident inquests regarding preventable traffic safety issues are addressed by traffic police → accidents caused by other factors will remain → accidents that happen due to preventable traffic safety issues are decreasing (conclusion)
Missing-link: Between percentage of accidents caused by drivers ignoring traffic lights declining this year and the conclusion that accidents that happen due to preventable traffic safety issues are decreasing
Expectation from the correct answer choice: Something on the lines of confusing the decline in the “percentage” of accidents of a particular type, among all accidents, with the decline in the “number” of the accidents of that type
Note: This argument commits the classic GMAT error of confusing “percentage” with “absolute numbers”; the city resident cites the decline in the “percentage” of accidents of a particular type, among all accidents, but draws a conclusion about the decline in the “number” of the accidents of that type. Besides, please be extra careful when you see numbers/percentages/proportions in CR questions; often, the key lies in the numbers.
A. Trap. This answer choice, suggesting that some accidents are likely not correctly attributed to drivers ignoring traffic lights, indicates underreporting of such accidents; this answer choice makes no suggestion regarding a specific timeline, suggesting that this answer choice indicates underreporting at all times in the past; so, underreporting is a common factor in the past years and in this year, thus failing to explain any difference in the proportion/number of such accidents in this year; hence, this answer choice is just additional information and does not weaken the argument. Furthermore, the flaw in the argument is that it confuses the decline in the “percentage” of accidents of a particular type, among all accidents, with the decline in the “number” of the accidents of that type; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Because this answer choice does not indicate the flaw in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. Correct. If there is a sharp rise in the number of accidents because of factors other than drivers ignoring traffic lights, the number of all accidents is likely to rise significantly; a large increase in the total number of accidents indicates that even if the percentage of accidents of a particular type declined, it does not necessarily indicate a decline in the number of such accidents (example: 10% of 100 is greater than 8% of 150); so, the possibility stated in this answer choice casts doubt on the conclusion that accidents that happen due to preventable traffic safety issues are decreasing; hence, failure to consider the sharp rise in the accidents caused by other factors is the flaw in the argument, as the answer choice mentions. Because this answer choice indicates the flaw in the argument, this answer choice is correct.
C. Trap. The argument is concerned with whether the accidents that happen due to preventable traffic safety issues are decreasing; the city resident cites inquests as the cause for this decline and not as a measure of the number of accidents; whether inquests are the most reliable way to ascertain the number of accidents has no bearing on the argument; so, failure to consider the possibility stated in this answer choice is not the flaw in the argument. Furthermore, the flaw in the argument is that it confuses the decline in the “percentage” of accidents of a particular type, among all accidents, with the decline in the “number” of the accidents of that type; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Because this answer choice does not indicate the flaw in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. Trap. The argument is concerned with whether the accidents that happen due to preventable traffic safety issues are decreasing; the city resident cites inquests as the cause for this decline; whether the number of inquests increased and what the cause for the increase was have no bearing on the argument; so, failure to consider the possibility stated in the answer choice is not the flaw in the argument. Furthermore, the flaw in the argument is that it confuses the decline in the “percentage” of accidents of a particular type, among all accidents, with the decline in the “number” of accidents of that type; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Because this answer choice does not indicate the flaw in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
E. Trap. What the city residents believe regarding particular accidents and their causes makes no suggestion regarding whether the accidents that happen due to preventable traffic safety issues are decreasing; so, this answer choice is just additional information and does not weaken the argument; hence, failure to consider the possibility stated in the answer choice is not the flaw in the argument. Furthermore, the flaw in the argument is that it confuses the decline in the “percentage” of accidents of a particular type, among all accidents, with the decline in the “number” of the accidents of that type; we need an answer choice on similar lines. Because this answer choice does not indicate the flaw in the argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
B is the best choice.
On the GMAT, dialogue-based Critical Reasoning questions test the same core skills as other formats. The difference lies in presentation, where the argument unfolds through a quick back-and-forth between two speakers. Your task is to judge the reasoning and answer the question.
Important: Before visiting the following sample question(s), if you would like a quick brush up of key CR Dialogue concepts, you may first visit: Free GMAT CR Dialogue Prep
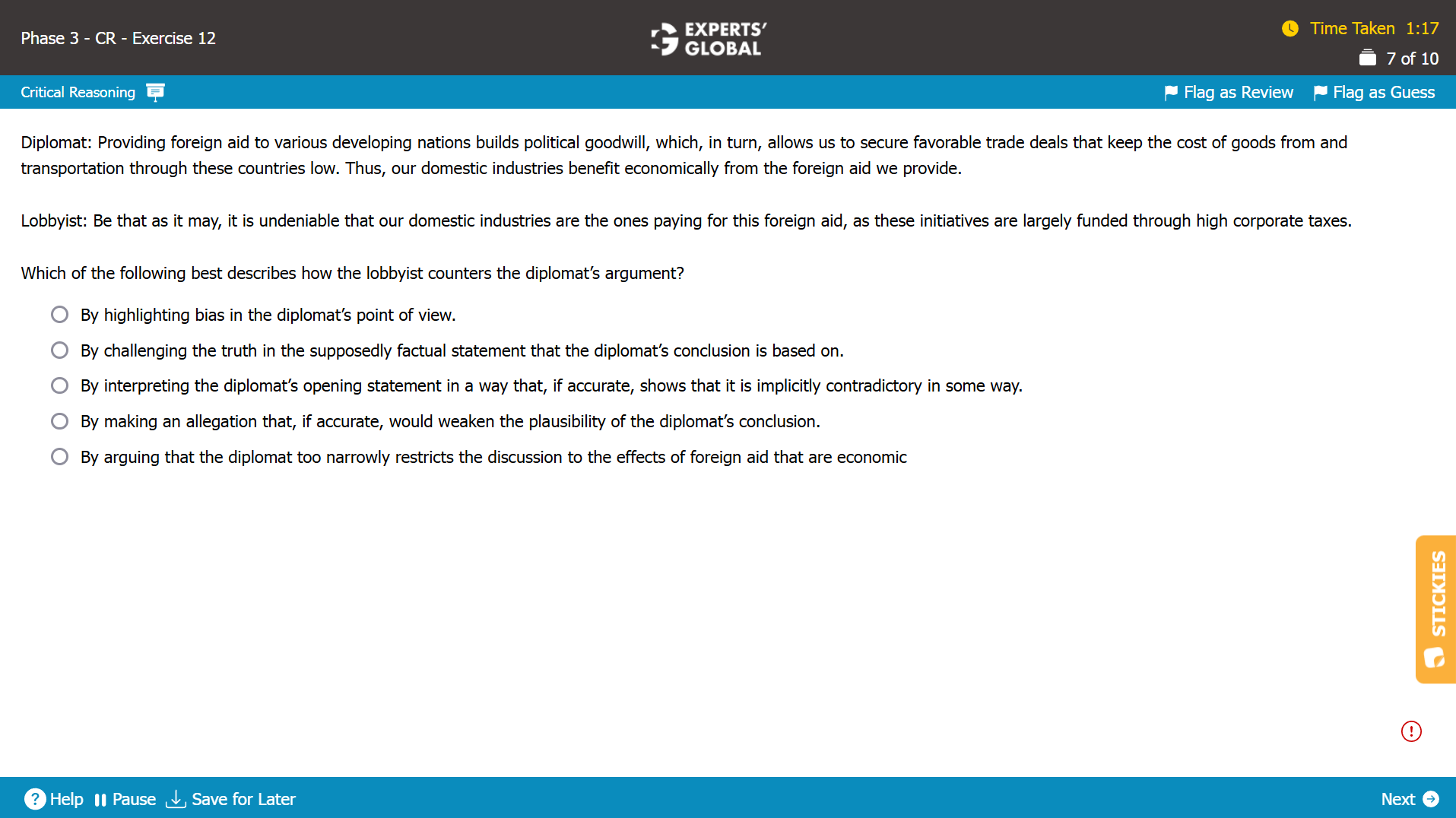
Show Explanation

Written Explanation
Mind-map: Diplomat: Aid to developing countries builds goodwill → facilitates favorable deals and keeps costs of goods low → domestic industries benefit economically → Lobbyist: foreign aid is funded through corporate taxes → domestic industries pay for the foreign aid
Missing-link: Not needed
Expectation from the correct answer choice: Something on the lines of finding a fault in the diplomat’s argument by introducing new information
A. The lobbyist simply accepts the facts provided by the diplomat and counters the diplomat’s argument by adding new information; however, the lobbyist does not suggest that the diplomat’s view is biased; so, it is incorrect to state that the lobbyists does so, as the answer choice mentions. Because this answer choice does not describe how the lobbyist counters the diplomat’s argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
B. Trap. The lobbyist responds to the diplomat’s argument by stating that “Be that as it may”, suggesting that the lobbyist accepts the facts provided by the diplomat but has a different opinion; so, it is incorrect to state that the lobbyist challenges the truth of the statement on which the diplomat’s conclusion is based, as the answer choice mentions. Because this answer choice does not describe how the lobbyist counters the diplomat’s argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
C. Trap. The lobbyist simply accepts the facts provided by the diplomat and counters the diplomat’s argument by adding new information; however, the lobbyist neither offers an interpretation of nor highlights a contradiction in the diploma’s statement; so, it is incorrect to state that the lobbyists does so, as the answer choice mentions. Because this answer choice does not describe how the lobbyist counters the diplomat’s argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
D. Correct. If domestic industries pay for the foreign aid as the lobbyist suggests, it casts doubt on the diplomat’s view that providing foreign aid to developing nations benefits domestic industries; thus, this answer choice aptly explains how the lobbyist counters the diplomat’s argument. Because this answer choice describes how the lobbyist counters the diplomat’s argument, this answer choice is correct.
E. Trap. Economic considerations are at the centre of the whole discussion, including the diplomat’s argument and the lobbyist’s response; so, it is incorrect to state that the discussion is “too narrowly restricted” to economic effects. Further, the lobbyist’s argument that “domestic industries are the ones paying for this foreign aid” is based on an economic concern, suggesting that the lobbyist is not likely to term the diplomat’s economic concern “too narrowly restricted”. Because this answer choice does not describe how the lobbyist counters the diplomat’s argument, this answer choice is incorrect.
D is the best choice.
15 full-length GMAT practice tests (includes a free test)
End-to-end GMAT prep course online (includes 7-day free trial)