Invest 30 seconds...
...for what may lead to a life altering association!
Help Line
- +91.8800.2828.00 (IND)
- 1030-1830 Hrs IST, Mon-Sat
- support@expertsglobal.com
...for what may lead to a life altering association!


On GMAT Critical Reasoning, false analogy means assuming two things are alike in important respects, so a claim for one must hold for the other. Simple example: Both smoothies and sodas are cold and sweet; therefore, soda is as healthy as a fruit smoothie. Be careful.
Analogies can clarify reasoning when similarities are relevant and proportional. This overview introduces how GMAT Critical Reasoning evaluates analogical claims: identify what is being compared, specify the property transferred, and test whether contexts, mechanisms, and constraints align. You’ll see how to separate sound parallels from superficial ones, setting up the video and the stepwise article that follows. The same habit supports disciplined argument appraisal in GMAT prep and evidence-based comparison in MBA admissions, where structure matters more than surface resemblance.

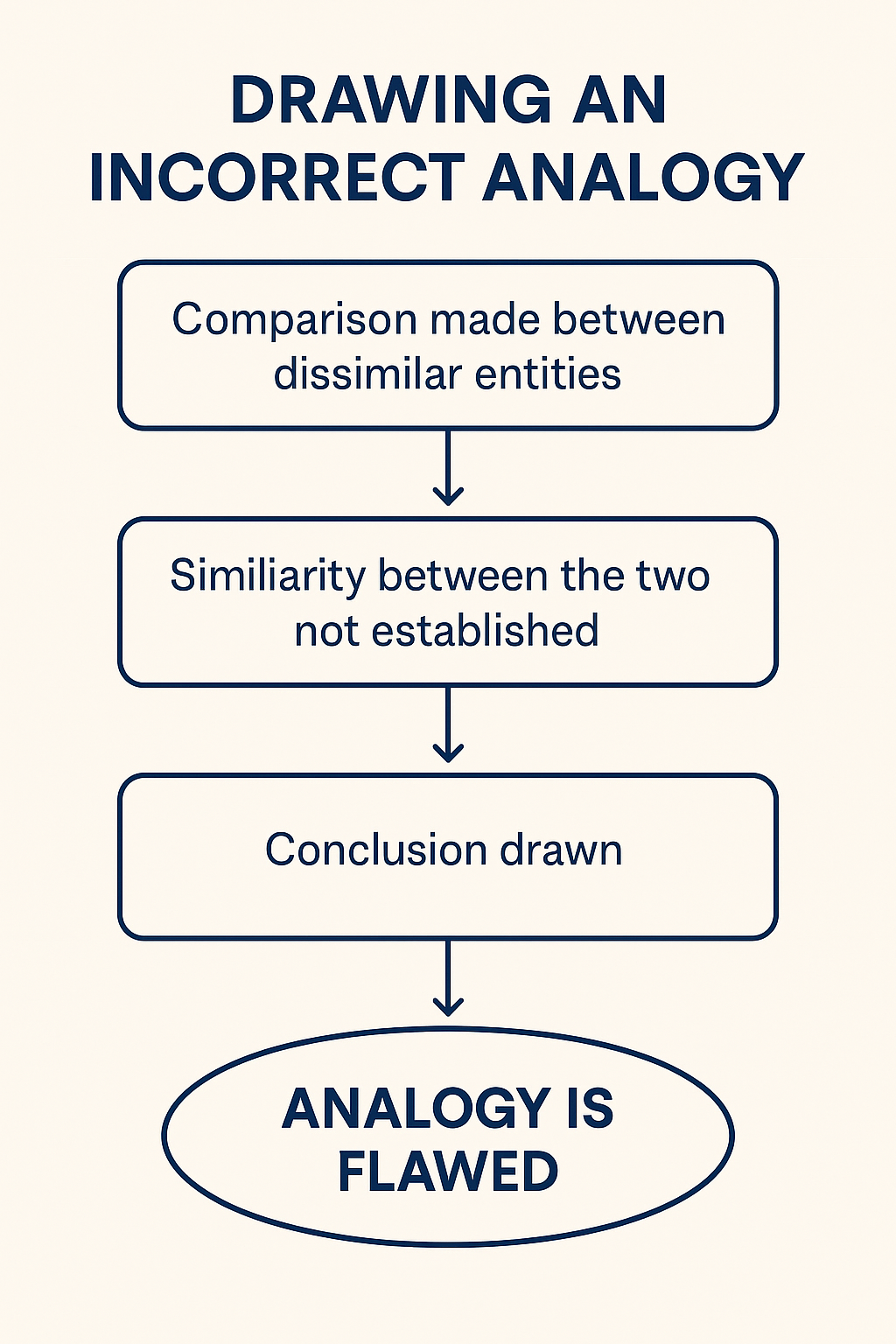
An analogy becomes flawed when a conclusion is drawn by comparing two entities without proving that they are indeed similar in the relevant context. This error often appears subtle but can completely invalidate the reasoning. The GMAT frequently uses such flawed analogies to test whether students are alert to hidden weaknesses in arguments.

Consider the following…
When Xaku was struggling with a budget deficit, it endorsed foreign direct investments and achieved good progress in alleviating its budget deficit. Sontario is struggling with budget deficit; the Sontarian government must endorse foreign direct investments in Sontario.
The reasoning is flawed because it fails to establish that the two countries are comparable in their political systems, economic structures, or social dynamics. Without demonstrating similarity, this is argument suffers from the false analogy fallacy.
Now, consider the following…
When Xaku was struggling with a budget deficit, it endorsed foreign direct investments and achieved good progress in alleviating its budget deficit. Sontario is struggling with a budget deficit. The sociopolitical and geoeconomics conditions of Sontario are similar to those of Xaku when it endorsed foreign direct investment. The Sontarian government must consider endorsing foreign direct investments in Sontario.
In this case, the analogy is reasonable because the similarities have been explicitly established.
Drawing an analogy itself is not a flaw. The flaw arises only when the entities being compared are insufficiently similar or when no attempt has been made to prove similarity. The GMAT expects students to check whether the comparison stands on solid ground or merely rests on assumption.
When encountering such questions, ask yourself:
Step 1: Review the question stem first to lock in the exact requirement.
Step 2: Work through the reasoning carefully; draft a Mind map and surface the missing link.
Step 3: Articulate your broad expectation from the correct answer choice.
Step 4: Rule out four choices; the choice that remains is your answer.
Verify once more before you confirm.

This article center on recognizing when an argument relies on an incorrect analogy. A flawed analogy assumes that sharing one trait implies similarity in all relevant respects, which is often not justified. The skill lies in checking whether proper comparability has been established before accepting the conclusion. Practicing this distinction through GMAT simulations trains you to identify strong versus weak parallels, improving accuracy in Critical Reasoning and enhancing logical clarity essential for academic and professional decisions.
Reasoning built on analogies reminds us that while comparisons can illuminate, they can also obscure if made without care. In GMAT preparation, discerning valid from flawed analogies strengthens not only accuracy but also judgment, a skill that echoes far beyond the test. In MBA applications, applicants often compare their experiences with broader themes, and in life, decisions are frequently justified by analogy. Learning to question whether parallels are real or forced builds intellectual honesty. Practicing with a GMAT mock nurtures this discipline, preparing you to approach arguments, choices, and ambitions with balanced and thoughtful clarity.